Allogeneic differences in the dependence on CD4+ T-cell help for virus-specific CD8+ T-cell differentiation
- PMID: 17913814
- PMCID: PMC2168883
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.01778-07
Allogeneic differences in the dependence on CD4+ T-cell help for virus-specific CD8+ T-cell differentiation
Abstract
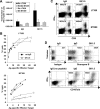
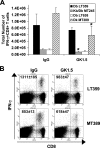
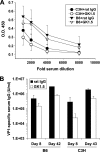
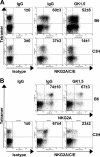
CD4(+) T-cell help enables antiviral CD8(+) T cells to differentiate into fully competent memory cells and sustains CD8(+) T-cell-mediated immunity during persistent virus infection. We recently reported that mice of C57BL/6 and C3H strains differ in their dependence on CD28 and CD40L costimulation for long-term control of infection by polyoma virus, a persistent mouse pathogen. In this study, we asked whether mice of these inbred strains also vary in their requirement for CD4(+) T-cell help for generating and maintaining polyoma virus-specific CD8(+) T cells. CD4(+) T-cell-depleted C57BL/6 mice mounted a robust antiviral CD8(+) T-cell response during acute infection, whereas unhelped CD8(+) T-cell effectors in C3H mice were functionally impaired during acute infection and failed to expand upon antigenic challenge during persistent infection. Using (C57BL/6 x C3H)F(1) mice, we found that the dispensability for CD4(+) T-cell help for the H-2(b)-restricted polyoma virus-specific CD8(+) T-cell response during acute infection extends to the H-2(k)-restricted antiviral CD8(+) T cells. Our findings demonstrate that dependence on CD4(+) T-cell help for antiviral CD8(+) T-cell effector differentiation can vary among allogeneic strains of inbred mice.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Costimulation requirements for antiviral CD8+ T cells differ for acute and persistent phases of polyoma virus infection.J Immunol. 2006 Feb 1;176(3):1814-24. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.176.3.1814. J Immunol. 2006. PMID: 16424212
-
MHC class Ib-restricted CD8 T cells differ in dependence on CD4 T cell help and CD28 costimulation over the course of mouse polyomavirus infection.J Immunol. 2012 Apr 1;188(7):3071-9. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1103554. Epub 2012 Mar 5. J Immunol. 2012. PMID: 22393155 Free PMC article.
-
The antiviral CD8+ T cell response is differentially dependent on CD4+ T cell help over the course of persistent infection.J Immunol. 2007 Jul 15;179(2):1113-21. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.179.2.1113. J Immunol. 2007. PMID: 17617604
-
Immunity to polyoma virus infection and tumorigenesis.Viral Immunol. 2001;14(3):199-216. doi: 10.1089/088282401753266738. Viral Immunol. 2001. PMID: 11572632 Review.
-
Pathogen-host standoff: immunity to polyomavirus infection and neoplasia.Immunol Res. 2004;29(1-3):139-50. doi: 10.1385/IR:29:1-3:139. Immunol Res. 2004. PMID: 15181277 Review.
Cited by
-
CD4+ T cell help has an epitope-dependent impact on CD8+ T cell memory inflation during murine cytomegalovirus infection.J Immunol. 2009 Sep 15;183(6):3932-41. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.0900227. Epub 2009 Aug 19. J Immunol. 2009. PMID: 19692644 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Andrews, N. P., C. D. Pack, V. Vezys, G. N. Barber, and A. E. Lukacher. 2007. Early virus-associated bystander events affect the fitness of the CD8 T cell response to persistent virus infection. J. Immunol. 178:7267-7275. - PubMed
-
- Baars, P. A., S. Sierro, R. Arens, K. Tesselaar, B. Hooibrink, P. Klenerman, and R. A. van Lier. 2005. Properties of murine CD8+CD27− T cells. Eur. J. Immunol. 35:3131-3141. - PubMed
-
- Badovinac, V. P., and J. T. Harty. 2007. Manipulating the rate of memory CD8+ T cell generation after acute infection. J. Immunol. 179:53-63. - PubMed
-
- Badovinac, V. P., K. A. Messingham, A. Jabbari, J. S. Haring, and J. T. Harty. 2005. Accelerated CD8+ T-cell memory and prime-boost response after dendritic-cell vaccination. Nat. Med. 11:748-756. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

