Extracellular signal-regulated kinase 2 (ERK2) knockdown mice show deficits in long-term memory; ERK2 has a specific function in learning and memory
- PMID: 17913910
- PMCID: PMC6672813
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0117-07.2007
Extracellular signal-regulated kinase 2 (ERK2) knockdown mice show deficits in long-term memory; ERK2 has a specific function in learning and memory
Abstract
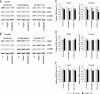
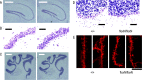
The extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) 1 and 2 are important signaling components implicated in learning and memory. These isoforms display a high degree of sequence homology and share a similar substrate profile. However, recent findings suggest that these isoforms may have distinct roles: whereas ERK1 seems to be not so important for associative learning, ERK2 might be critically involved in learning and memory. Thus, the individual role of ERK2 has received considerable attention, although it is yet to be understood. Here, we have generated a series of mice in which ERK2 expression decreased in an allele dose-dependent manner. Null ERK2 knock-out mice were embryonic lethal, and the heterozygous mice were anatomically impaired. To gain a better understanding of the influence of ERK2 on learning and memory, we also generated knockdown mice in which ERK2 expression was partially (20-40%) reduced. These mutant mice were viable and fertile with normal appearance. The mutant mice showed a deficit in long-term memory in classical fear conditioning, whereas short-term memory was normal. The mice also showed learning deficit in the water maze and the eight-arm radial maze. The ERK1 expression level of the knockdown mice was comparable with the wild-type control. Together, our results indicate a noncompensable role of ERK2-dependent signal transduction in learning and memory.
Figures



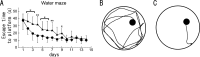
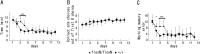

Similar articles
-
Sex-specific deficits in biochemical but not behavioral responses to delay fear conditioning in prenatal alcohol exposure mice.Neurobiol Learn Mem. 2018 Dec;156:1-16. doi: 10.1016/j.nlm.2018.10.002. Epub 2018 Oct 12. Neurobiol Learn Mem. 2018. PMID: 30316893 Free PMC article.
-
ERK2 contributes to the control of social behaviors in mice.J Neurosci. 2011 Aug 17;31(33):11953-67. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2349-11.2011. J Neurosci. 2011. PMID: 21849556 Free PMC article.
-
Reduced cortical BDNF expression and aberrant memory in Carf knock-out mice.J Neurosci. 2010 Jun 2;30(22):7453-65. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3997-09.2010. J Neurosci. 2010. PMID: 20519520 Free PMC article.
-
The neuronal MAP kinase cascade: a biochemical signal integration system subserving synaptic plasticity and memory.J Neurochem. 2001 Jan;76(1):1-10. doi: 10.1046/j.1471-4159.2001.00054.x. J Neurochem. 2001. PMID: 11145972 Review.
-
Epigenetic mechanisms in stress and adaptation.Brain Behav Immun. 2011 Oct;25(7):1305-15. doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2011.06.005. Epub 2011 Jun 14. Brain Behav Immun. 2011. PMID: 21704151 Review.
Cited by
-
Memory-related hippocampal brain-derived neurotrophic factor activation pathways from repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation in the 3xTg-AD mouse line.Exp Gerontol. 2023 Nov;183:112323. doi: 10.1016/j.exger.2023.112323. Epub 2023 Nov 1. Exp Gerontol. 2023. PMID: 39351497 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of Ketamine on LTP and NMDAR EPSC in Hippocampus of the Chronic Social Defeat Stress Mice Model of Depression.Front Behav Neurosci. 2018 Oct 9;12:229. doi: 10.3389/fnbeh.2018.00229. eCollection 2018. Front Behav Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 30356718 Free PMC article.
-
Neonatal administration of a subanaesthetic dose of JM-1232(-) in mice results in no behavioural deficits in adulthood.Sci Rep. 2021 Jun 18;11(1):12874. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-92344-3. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 34145371 Free PMC article.
-
Nicotinic acetylcholine receptor signalling: roles in Alzheimer's disease and amyloid neuroprotection.Pharmacol Rev. 2009 Mar;61(1):39-61. doi: 10.1124/pr.108.000562. Epub 2009 Mar 16. Pharmacol Rev. 2009. PMID: 19293145 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mitogen-activated protein kinase signalling and ERK1/2 bistability in asthma.Clin Exp Allergy. 2011 Feb;41(2):149-59. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2222.2010.03658.x. Epub 2010 Dec 1. Clin Exp Allergy. 2011. PMID: 21121982 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Abel T, Lattal KM. Molecular mechanisms of memory acquisition, consolidation and retrieval. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2001;11:180–187. - PubMed
-
- Adams JP, Sweatt JD. Molecular psychology: roles for the ERK MAP kinase cascade in memory. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 2002;42:135–163. - PubMed
-
- Atkins CM, Selcher JC, Petraitis JJ, Trzaskos JM, Sweatt JD. The MAPK cascade is required for mammalian associative learning. Nat Neurosci. 1998;1:602–609. - PubMed
-
- Bading H, Greenberg ME. Stimulation of protein tyrosine phosphorylation by NMDA receptor activation. Science. 1991;253:912–914. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
