Moderate reduction of gamma-secretase attenuates amyloid burden and limits mechanism-based liabilities
- PMID: 17913918
- PMCID: PMC6672827
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2152-07.2007
Moderate reduction of gamma-secretase attenuates amyloid burden and limits mechanism-based liabilities
Abstract
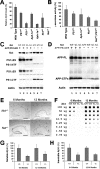
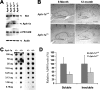
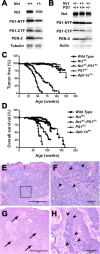
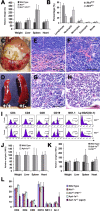
Although gamma-secretase is recognized as a therapeutic target for Alzheimer's disease, side effects associated with strong inhibition of this aspartyl protease raised serious concerns regarding this therapeutic strategy. However, it is not known whether moderate inhibition of this enzyme will allow dissociation of beneficial effects in the CNS from mechanism-based toxicities in the periphery. We tested this possibility by using a series of mice with genetic reduction of gamma-secretase (levels ranging from 25 to 64% of control mice). Here, we document that even 30% reduction of gamma-secretase can effectively ameliorate amyloid burden in the CNS. However, global reduction of this enzyme below a threshold level increased the risk of developing squamous cell carcinoma as well as abnormal proliferation of granulocytes in a gamma-secretase dosage-dependent manner. Importantly, we demonstrate that there exists a critical gamma-secretase level that reduces the risk of amyloidosis in the CNS and limits tumorigenesis in epithelia. Our findings suggest that moderate inhibition of gamma-secretase represents an attractive anti-amyloid therapy for Alzheimer's disease.
Figures

Comment in
-
Moderate reduction of gamma-secretase: is there a therapeutic sweet spot?J Neurosci. 2007 Dec 12;27(50):13579-80. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4821-07.2007. J Neurosci. 2007. PMID: 18077669 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Allman D, Punt JA, Izon DJ, Aster JC, Pear WS. An invitation to T and more: Notch signaling in lymphopoiesis. Cell. 2002;109:S1–S11. - PubMed
-
- Artavanis-Tsakonas S, Rand MD, Lake RJ. Notch signaling: cell fate control and signal integration in development. Science. 1999;284:770–776. - PubMed
-
- Barten DM, Guss VL, Corsa JA, Loo A, Hansel SB, Zheng M, Munoz B, Srinivasan K, Wang B, Robertson BJ, Polson CT, Wang J, Roberts SB, Hendrick JP, Anderson JJ, Loy JK, Denton R, Verdoorn TA, Smith DW, Felsenstein KM. Dynamics of β-amyloid reductions in brain, cerebrospinal fluid, and plasma of β-amyloid precursor protein transgenic mice treated with a γ-secretase inhibitor. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2005;312:635–643. - PubMed
-
- Birchler JA, Riddle NC, Auger DL, Veitia RA. Dosage balance in gene regulation: biological implications. Trends Genet. 2005;21:219–226. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
