Corticobasal syndrome and primary progressive aphasia as manifestations of LRRK2 gene mutations
- PMID: 17914064
- PMCID: PMC3619720
- DOI: 10.1212/01.WNL.0000280574.17166.26
Corticobasal syndrome and primary progressive aphasia as manifestations of LRRK2 gene mutations
Abstract
Background: Mutations in the LRRK2 gene are an important cause of familial and nonfamilial parkinsonism. Despite pleomorphic pathology, LRRK2 mutations are believed to manifest clinically as typical Parkinson disease (PD). However, most genetic screens have been limited to PD clinic populations.
Objective: To clinically characterize LRRK2 mutations in cases recruited from a spectrum of neurodegenerative diseases.
Methods: We screened for the common G2019S mutation and several additional previously reported LRRK2 mutations in 434 individuals. A total of 254 patients recruited from neurodegenerative disease clinics and 180 neurodegenerative disease autopsy cases from the University of Pennsylvania brain bank were evaluated.
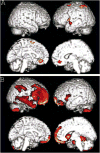
Results: Eight cases were found to harbor a LRRK2 mutation. Among patients with a mutation, two presented with cognitive deficits leading to clinical diagnoses of corticobasal syndrome and primary progressive aphasia.
Conclusion: The clinical presentation of LRRK2-associated neurodegenerative disease may be more heterogeneous than previously assumed.
Figures
Comment in
-
Corticobasal syndrome and primary progressive aphasia as manifestations of lrrk2 gene mutations.Neurology. 2008 Jul 22;71(4):303; author reply 303-4. doi: 10.1212/01.wnl.0000320511.30222.dd. Neurology. 2008. PMID: 18645174 No abstract available.
References
-
- Gilks WP, Abou-Sleiman PM, Gandhi S, et al. A common LRRK2 mutation in idiopathic Parkinson's disease. Lancet. 2005;365:415–416. - PubMed
-
- Lesage S, Durr A, Tazir M, et al. LRRK2 G2019S as a cause of Parkinson's disease in North African Arabs. N Engl J Med. 2006;354:422–423. - PubMed
-
- Ozelius LJ, Senthil G, Saunders-Pullman R, et al. LRRK2 G2019S as a cause of Parkinson's disease in Ashkenazi Jews. N Engl J Med. 2006;354:424–425. - PubMed
-
- Zimprich A, Biskup S, Leitner P, et al. Mutations in LRRK2 cause autosomal-dominant parkinsonism with pleomorphic pathology. Neuron. 2004;44:601–607. - PubMed
-
- Paisan-Ruiz C, Lang AE, Kawarai C, et al. LRRK2 gene in Parkinson disease: Mutation analysis and case control association study. Neurology. 2005;65:696–700. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 NS044266/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG010124/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AG17586/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AG017586/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AG011542/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS44266/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P50 NS053488/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AG019724/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AG014449/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AG014382/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AG14382/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG10124/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AG14449/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AG009215/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG15116/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG015116/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AG19724/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AG09215/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AG11542/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- K08 AG033101/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
