Top-down proteomics on a chromatographic time scale using linear ion trap fourier transform hybrid mass spectrometers
- PMID: 17915963
- PMCID: PMC2361135
- DOI: 10.1021/ac070553t
Top-down proteomics on a chromatographic time scale using linear ion trap fourier transform hybrid mass spectrometers
Abstract
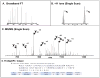
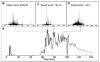
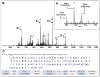
Proteomics has grown significantly with the aid of new technologies that consistently are becoming more streamlined. While processing of proteins from a whole cell lysate is typically done in a bottom-up fashion utilizing MS/MS of peptides from enzymatically digested proteins, top-down proteomics is becoming a viable alternative that until recently has been limited largely to offline analysis by tandem mass spectrometry. Here we describe a method for high-resolution tandem mass spectrometery of intact proteins on a chromatographic time scale. In a single liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) run, we have identified 22 yeast proteins with molecular weights from 14 to 35 kDa. Using anion exchange chromatography to fractionate a whole cell lysate before online LC-MS/MS, we have detected 231 metabolically labeled (14N/15N) protein pairs from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Thirty-nine additional proteins were identified and characterized from LC-MS/MS of selected anion exchange fractions. Automated localization of multiple acetylations on Histone H4 was also accomplished on an LC time scale from a complex protein mixture. To our knowledge, this is the first demonstration of top-down proteomics (i.e., many identifications) on linear ion trap Fourier transform (LTQ FT) systems using high-resolution MS/MS data obtained on a chromatographic time scale.
Figures


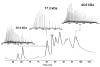
References
-
- Wang J, Li D, Dangott LJ, Wu G. J Nutr. 2006;136:1759–1762. - PubMed
-
- Schulenborg T, Schmidt O, van Hall A, Meyer HE, Hamacher M, Marcus K. J Neural Transm. 2006;113:1055–1073. - PubMed
-
- Gorg A, Obermaier C, Boguth G, Harder A, Scheibe B, Wildgruber R, Weiss W. Electrophoresis. 2000;21:1037–1053. - PubMed
-
- Rabilloud T. Proteomics. 2002;2:3–10. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

