Krit 1 interactions with microtubules and membranes are regulated by Rap1 and integrin cytoplasmic domain associated protein-1
- PMID: 17916086
- PMCID: PMC2580780
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1742-4658.2007.06068.x
Krit 1 interactions with microtubules and membranes are regulated by Rap1 and integrin cytoplasmic domain associated protein-1
Abstract
The small G protein Rap1 regulates diverse cellular processes such as integrin activation, cell adhesion, cell-cell junction formation and cell polarity. It is crucial to identify Rap1 effectors to better understand the signalling pathways controlling these processes. Krev interaction trapped 1 (Krit1), a protein with FERM (band four-point-one/ezrin/radixin/moesin) domain, was identified as a Rap1 partner in a yeast two-hybrid screen, but this interaction was not confirmed in subsequent studies. As the evidence suggests a role for Krit1 in Rap1-dependent pathways, we readdressed this question. In the present study, we demonstrate by biochemical assays that Krit1 interacts with Rap1A, preferentially its GTP-bound form. We show that, like other FERM proteins, Krit1 adopts two conformations: a closed conformation in which its N-terminal NPAY motif interacts with its C-terminus and an opened conformation bound to integrin cytoplasmic domain associated protein (ICAP)-1, a negative regulator of focal adhesion assembly. We show that a ternary complex can form in vitro between Krit1, Rap1 and ICAP-1 and that Rap1 binds the Krit1 FERM domain in both closed and opened conformations. Unlike ICAP-1, Rap1 does not open Krit1. Using sedimentation assays, we show that Krit1 binds in vitro to microtubules through its N- and C-termini and that Rap1 and ICAP-1 inhibit Krit1 binding to microtubules. Consistently, YFP-Krit1 localizes on cyan fluorescent protein-labelled microtubules in baby hamster kidney cells and is delocalized from microtubules upon coexpression with activated Rap1V12. Finally, we show that Krit1 binds to phosphatidylinositol 4,5-P(2)-containing liposomes and that Rap1 enhances this binding. Based on these results, we propose a model in which Krit1 would be delivered by microtubules to the plasma membrane where it would be captured by Rap1 and ICAP-1.
Figures
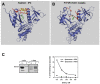

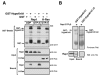
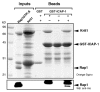


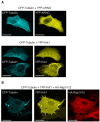

References
-
- Bos JL. Linking Rap to cell adhesion. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2005;17:123–8. - PubMed
-
- Caron E. Cellular functions of the Rap1 GTP-binding protein: a pattern emerges. J Cell Sci. 2003;116:435–440. - PubMed
-
- Kooistra MR. Rap1: a key regulator in cell-cell junction formation. J Cell Sci. 2007;120:17–22. - PubMed
-
- Katagiri K. RAPL, a Rap1-binding molecule that mediates Rap1-induced adhesion through spatial regulation of LFA-1. Nat Immunol. 2003;6:6. - PubMed
-
- Lafuente EM. RIAM, an Ena/VASP and Profilin ligand, interacts with Rap1-GTP and mediates Rap1-induced adhesion. Dev Cell. 2004;7:585–95. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

