Viral and host factors induce macrophage activation and loss of toll-like receptor tolerance in chronic HCV infection
- PMID: 17916356
- PMCID: PMC2593079
- DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2007.08.003
Viral and host factors induce macrophage activation and loss of toll-like receptor tolerance in chronic HCV infection
Abstract
Background & aims: Persistent inflammation contributes to progression of liver damage in chronic HCV (cHCV) infection. Repeated exposure to toll-like receptor (TLR) ligands results in tolerance, a protective mechanism aimed at limiting inflammation.
Methods: Monocytes/macrophages were repeatedly stimulated via proinflammatory cytokine-inducing TLRs and evaluated for activation markers.
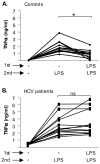
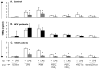
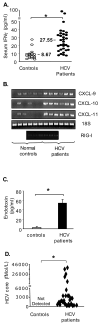
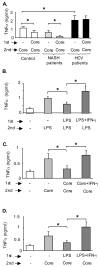
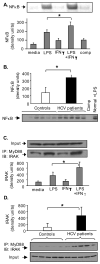
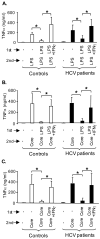
Results: Unlike monocytes of controls or patients with nonalcoholic steatohepatitis, the monocytes of cHCV patients were hyperresponsive and failed to show homo- or heterotolerance to TLR ligands, manifested by elevated tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-alpha production. Serum levels of interferon (IFN)-gamma, endotoxin (TLR4 ligand), and HCV core protein (TLR2 ligand) were elevated in cHCV patients suggesting potential mechanisms for in vivo monocyte preactivation. Treatment of normal monocytes with IFN-gamma resulted in loss of tolerance to lipopolysaccharide (LPS) or HCV core protein. Furthermore, we found increased levels of MyD88-IRAK1 complexes and nuclear factor (NF)-kappaB activity both in monocytes of cHCV patients and in normal monocytes that lost TLR tolerance after IFN-gamma + LPS pretreatment. In vitro differentiation of TLR non-tolerant cHCV monocytes into macrophages restored their capacity to exhibit TLR tolerance to LPS and HCV core protein, and this could be reversed by administration of IFN-gamma. cHCV patients exhibited increased TNF-alpha in the circulation and in the liver. In cHCV livers, we found Kupffer cell/macrophage activation indicated by increased CD163 and CD33 expression.
Conclusions: We identified that host-derived factors (IFN-gamma and endotoxin) and viral factors (HCV core protein) act in tandem to induce and maintain monocyte/macrophage activation, thus favoring persistent inflammation in patients with cHCV infection.
Figures

References
-
- Kim WR, Brown RS, Jr, Terrault NA, El-Serag H. Burden of liver disease in the United States: summary of a workshop. Hepatology. 2002;36:227–242. - PubMed
-
- Neuman MG, Benhamou JP, Malkiewicz IM, Ibrahim A, Valla DC, Martinot-Peignoux M, Asselah T, Bourliere M, Katz GG, Shear NH, Marcellin P. Kinetics of serum cytokines reflect changes in the severity of chronic hepatitis C presenting minimal fibrosis. J Viral Hepat. 2002;9:134–140. - PubMed
-
- Takeda K, Kaisho T, Akira S. Toll-like receptors. Ann Rev Immunol. 2003;21:335–376. - PubMed
-
- Bartenschlager R, Frese M, Pietschmann T. Novel insights into hepatitis C virus replication and persistence. Adv Virus Res. 2004;63:71–180. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

