pH dependence of melanoma cell migration: protons extruded by NHE1 dominate protons of the bulk solution
- PMID: 17916606
- PMCID: PMC2230576
- DOI: 10.1113/jphysiol.2007.145185
pH dependence of melanoma cell migration: protons extruded by NHE1 dominate protons of the bulk solution
Abstract
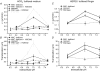
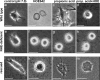
Migration and morphology of human melanoma cells (MV3) depend on extracellular pH (pHe) and the activity of the Na+/H+ exchanger NHE1. To distinguish effects of NHE1 activity per se from effects of pHe we compared an NHE1-deficient mutant with rescued and wild-type cells. Time lapse video microscopy was used to investigate migratory and morphological effects caused by pHe and NHE1 activity, and a membrane-bound fluorescein conjugate was employed for ratiometric pH measurements at the outer leaflet of the cell membrane. As long as NHE1 remained inactive due to deficiency or inhibition by cariporide (HOE642) neither migration nor morphology was affected by changes in pHe. Under these conditions pH at the outer leaflet of the plasma membrane was uniform all over the cell surface. The typical pH dependence of MV3 cell migration and morphology could be reconstituted by restoring NHE1 activity. At the same time the proton gradient at the outer leaflet of the plasma membrane with the higher proton concentration at the leading edge and the lower one at the cell rear was re-established as well. Hence, NHE1 activity generates a proton gradient at the cell surface accompanied by the cells' ability to respond to changes in pHe (bulk pH). We conclude that NHE1 activity contributes to the generation of a well-defined cell surface pH by creating a proton gradient at the outer leaflet of the plasma membrane that is needed for (i) the development of a variety of morphologies including a distinct polarity and (ii) migration. A missing proton gradient at the cell surface cannot be compensated for by varying pHe.
Figures


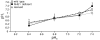
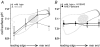
Similar articles
-
pH nanoenvironment at the surface of single melanoma cells.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2007;20(5):679-86. doi: 10.1159/000107550. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2007. PMID: 17762194
-
Intracellular pH gradients in migrating cells.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2011 Mar;300(3):C490-5. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00280.2010. Epub 2010 Dec 9. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2011. PMID: 21148407
-
The Na+ /H+ -exchanger (NHE1) generates pH nanodomains at focal adhesions.J Cell Physiol. 2013 Jun;228(6):1351-8. doi: 10.1002/jcp.24293. J Cell Physiol. 2013. PMID: 23184727
-
Protons extruded by NHE1: digestive or glue?Eur J Cell Biol. 2008 Sep;87(8-9):591-9. doi: 10.1016/j.ejcb.2008.01.007. Epub 2008 Mar 6. Eur J Cell Biol. 2008. PMID: 18328592 Review.
-
Na+-H+ exchanger, pH regulation and cancer.Recent Pat Anticancer Drug Discov. 2013 Jan 1;8(1):85-99. doi: 10.2174/15748928130108. Recent Pat Anticancer Drug Discov. 2013. PMID: 22738122 Review.
Cited by
-
The impact of tumour pH on cancer progression: strategies for clinical intervention.Explor Target Antitumor Ther. 2020;1(2):71-100. doi: 10.37349/etat.2020.00005. Epub 2020 Apr 28. Explor Target Antitumor Ther. 2020. PMID: 36046070 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CD44 targets Na(+)/H(+) exchanger 1 to mediate MDA-MB-231 cells' metastasis via the regulation of ERK1/2.Br J Cancer. 2014 Feb 18;110(4):916-27. doi: 10.1038/bjc.2013.809. Epub 2014 Jan 16. Br J Cancer. 2014. PMID: 24434427 Free PMC article.
-
Acidic extracellular pH promotes activation of integrin α(v)β(3).PLoS One. 2011 Jan 19;6(1):e15746. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0015746. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 21283814 Free PMC article.
-
Protons make tumor cells move like clockwork.Pflugers Arch. 2009 Sep;458(5):981-92. doi: 10.1007/s00424-009-0677-8. Epub 2009 May 13. Pflugers Arch. 2009. PMID: 19437033 Review.
-
Hypoxia and Extracellular Acidification as Drivers of Melanoma Progression and Drug Resistance.Cells. 2021 Apr 9;10(4):862. doi: 10.3390/cells10040862. Cells. 2021. PMID: 33918883 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bailey J, Gingell D. Contacts of chick fibroblasts on glass: results and limitations of quantitative interferometry. J Cell Sci. 1988;90:215–224. - PubMed
-
- Bernstein BW, Painter WB, Chen H, Minamide LS, Abe H, Bamburg JR. Intracellular pH modulation of ADF/cofilin proteins. Cell Motil Cytoskeleton. 2000;47:319–336. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

