NOS isoform-specific regulation of basal but not exercise-induced mitochondrial biogenesis in mouse skeletal muscle
- PMID: 17916611
- PMCID: PMC2375470
- DOI: 10.1113/jphysiol.2007.141309
NOS isoform-specific regulation of basal but not exercise-induced mitochondrial biogenesis in mouse skeletal muscle
Abstract
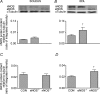
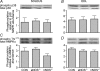
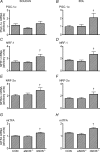
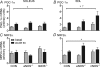
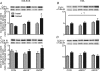
Nitric oxide is a potential regulator of mitochondrial biogenesis. Therefore, we investigated if mice deficient in endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS-/-) or neuronal NOS (nNOS-/-) have attenuated activation of skeletal muscle mitochondrial biogenesis in response to exercise. eNOS-/-, nNOS-/- and C57Bl/6 (CON) mice (16.3 +/- 0.2 weeks old) either remained in their cages (basal) or ran on a treadmill (16 m min(-1), 5% grade) for 60 min (n = 8 per group) and were killed 6 h after exercise. Other eNOS-/-, nNOS-/- and CON mice exercise trained for 9 days (60 min per day) and were killed 24 h after the last bout of exercise training. eNOS-/- mice had significantly higher nNOS protein and nNOS-/- mice had significantly higher eNOS protein in the EDL, but not the soleus. The basal mitochondrial biogenesis markers NRF1, NRF2alpha and mtTFA mRNA were significantly (P< 0.05) higher in the soleus and EDL of nNOS-/- mice whilst basal citrate synthase activity was higher in the soleus and basal PGC-1alpha mRNA higher in the EDL. Also, eNOS-/- mice had significantly higher basal citrate synthase activity in the soleus but not the EDL. Acute exercise increased (P< 0.05) PGC-1alpha mRNA in soleus and EDL and NRF2alpha mRNA in the EDL to a similar extent in all genotypes. In addition, short-term exercise training significantly increased cytochrome c protein in all genotypes (P< 0.05) in the EDL. In conclusion, eNOS and nNOS are differentially involved in the basal regulation of mitochondrial biogenesis in skeletal muscle but are not critical for exercise-induced increases in mitochondrial biogenesis in skeletal muscle.
Figures
Comment in
-
Really different knockout strains in movement?J Physiol. 2008 Feb 1;586(3):913; author reply 915-6. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2007.149948. Epub 2007 Dec 20. J Physiol. 2008. PMID: 18096594 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Akimoto T, Pohnert SC, Li P, Zhang M, Gumbs C, Rosenberg PB, Williams RS, Yan Z. Exercise stimulates Pgc-1α transcription in skeletal muscle through activation of the p38 MAPK pathway. J Biol Chem. 2005;280:19587–19593. - PubMed
-
- Altschul SF, Gish W, Miller W, Myers EW, Lipman DJ. Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol. 1990;215:403–410. - PubMed
-
- Balon TW, Nadler JL. Nitric oxide release is present from incubated skeletal muscle preparations. J Appl Physiol. 1994;77:2519–2521. - PubMed
-
- Biecker E, Neef M, Sagesser H, Shaw S, Koshy A, Reichen J. Nitric oxide synthase 1 is partly compensating for nitric oxide synthase 3 deficiency in nitric oxide synthase 3 knock-out mice and is elevated in murine and human cirrhosis. Liver Int. 2004;24:345–353. - PubMed
-
- Choate JK, Danson EJ, Morris JF, Paterson DJ. Peripheral vagal control of heart rate is impaired in neuronal NOS knockout mice. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2001;281:H2310–H2317. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

