The factor VIII C1 domain contributes to platelet binding
- PMID: 17916745
- PMCID: PMC2200805
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2007-01-068957
The factor VIII C1 domain contributes to platelet binding
Abstract
Activated factor VIII (FVIIIa) forms a procoagulant complex with factor IXa on negatively charged membranes, including activated platelet surfaces. Membrane attachment involves the FVIII C2 domain; involvement of the adjacent C1 domain has not been established. Binding of recombinant FVIII C1C2 and C2 proteins to platelets was detected by flow cytometry using (1) anti-C2 monoclonal antibody ESH8 followed by a phycoerythrin-labeled secondary antibody; (2) biotinylated C1C2 detected by phycoerythrin-labeled streptavidin, and (3) C1C2 and C2 site-specifically labeled with fluorescein. Highest binding and lowest background were obtained using fluorescein-conjugated proteins. More than 90% of activated platelets bound C1C2, compared with approximately 50% for equimolar C2. Estimates using fluorescent microbeads indicated approximately 7,000 C1C2-binding sites per platelet, approximately 1,400 for C2, and approximately 3,000 for fluorescein-labeled FVIIIa. Unlike C2 or FVIII(a), C1C2 bound to approximately 700 sites/platelet before activation. C1C2 binding to activated platelets appeared independent of von Willebrand factor and was competed effectively by FVIII(a), but only partially by excess C2. Fluorescein-labeled FVIIIa was competed much more effectively by C1C2 than C2 for binding to activated platelets. Two monoclonal antibodies that inhibit C2 binding to membranes competed platelet binding of C2 more effectively than C1C2. Thus, the C1 domain of FVIII contributes to platelet-binding affinity.
Figures



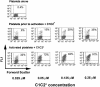
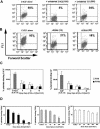
 ) or FVIIIa (
) or FVIIIa ( ); controls are shown as (
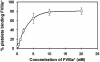
); controls are shown as ( ). Before competition, binding was near saturation for C1C2* and for C2*; however, note the different scales for the left and right panels, which indicate that binding of C2* to activated platelets was lower than for C1C2*. Data represent the mean and standard deviations (upper error bars shown) for measurements using 6 different platelet preparations. Representative data for one of the C1C2* competition experiments plotted in histogram and scattergram format are available in Figure S1A,B, available on the Blood website; see the Supplemental Figure link at the top of the online article. (D) FVIIIa* competition by FVIIIa, C1C2, or C2: 10 nM FVIIIa* (near-saturation binding, Figure 5) was competed by FVIIIa (left panel,
). Before competition, binding was near saturation for C1C2* and for C2*; however, note the different scales for the left and right panels, which indicate that binding of C2* to activated platelets was lower than for C1C2*. Data represent the mean and standard deviations (upper error bars shown) for measurements using 6 different platelet preparations. Representative data for one of the C1C2* competition experiments plotted in histogram and scattergram format are available in Figure S1A,B, available on the Blood website; see the Supplemental Figure link at the top of the online article. (D) FVIIIa* competition by FVIIIa, C1C2, or C2: 10 nM FVIIIa* (near-saturation binding, Figure 5) was competed by FVIIIa (left panel,  ), C1C2 (center panel,
), C1C2 (center panel,  ), or C2 (right panel,
), or C2 (right panel,  ) at molar ratios as indicated. Data represent the mean and standard deviations (upper error bars shown) for measurements using 5 (for right and center panels) and 4 (for left panel) different platelet preparations. Representative data from one of the FVIIIa*-C1C2 competition experiments plotted in histogram and scattergram format are available in Figure S1C,D.
) at molar ratios as indicated. Data represent the mean and standard deviations (upper error bars shown) for measurements using 5 (for right and center panels) and 4 (for left panel) different platelet preparations. Representative data from one of the FVIIIa*-C1C2 competition experiments plotted in histogram and scattergram format are available in Figure S1C,D.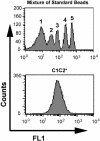
Similar articles
-
Activation of factor VIII by thrombin increases its affinity for binding to synthetic phospholipid membranes and activated platelets.J Biol Chem. 1998 Oct 23;273(43):27918-26. doi: 10.1074/jbc.273.43.27918. J Biol Chem. 1998. PMID: 9774404
-
Structural and functional characterization of platelet receptor-mediated factor VIII binding.J Biol Chem. 2000 Apr 28;275(17):13071-81. doi: 10.1074/jbc.275.17.13071. J Biol Chem. 2000. PMID: 10777612
-
Replacing the factor VIII C1 domain with a second C2 domain reduces factor VIII stability and affinity for factor IXa.J Biol Chem. 2013 Oct 25;288(43):31289-97. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.497289. Epub 2013 Sep 12. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 24030831 Free PMC article.
-
Role of activation of the coagulation factor VIII in interaction with vWf, phospholipid, and functioning within the factor Xase complex.Trends Cardiovasc Med. 1999 Oct;9(7):185-92. doi: 10.1016/s1050-1738(00)00019-0. Trends Cardiovasc Med. 1999. PMID: 10881749 Review.
-
The protein structure and effect of factor VIII.Thromb Res. 2007;119(1):1-13. doi: 10.1016/j.thromres.2005.12.015. Epub 2006 Feb 17. Thromb Res. 2007. PMID: 16487577 Review.
Cited by
-
Stable binding to phosphatidylserine-containing membranes requires conserved arginine residues in tandem C domains of blood coagulation factor VIII.Front Mol Biosci. 2022 Oct 26;9:1040106. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2022.1040106. eCollection 2022. Front Mol Biosci. 2022. PMID: 36387287 Free PMC article.
-
Atomistic Mechanism of Lipid Membrane Binding for Blood Coagulation Factor VIII with Molecular Dynamics Simulations on a Microsecond Time Scale.J Phys Chem B. 2025 Feb 6;129(5):1486-1498. doi: 10.1021/acs.jpcb.4c06575. Epub 2025 Jan 22. J Phys Chem B. 2025. PMID: 39840640 Free PMC article.
-
Phospholipid binding improves plasma survival of factor VIII.Thromb Haemost. 2010 Nov;104(5):1073-5. doi: 10.1160/TH10-06-0422. Epub 2010 Sep 13. Thromb Haemost. 2010. PMID: 20838749 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
High-affinity, noninhibitory pathogenic C1 domain antibodies are present in patients with hemophilia A and inhibitors.Blood. 2016 Oct 20;128(16):2055-2067. doi: 10.1182/blood-2016-02-701805. Epub 2016 Jul 5. Blood. 2016. PMID: 27381905 Free PMC article.
-
Structure of the factor VIII C2 domain in a ternary complex with 2 inhibitor antibodies reveals classical and nonclassical epitopes.Blood. 2013 Dec 19;122(26):4270-8. doi: 10.1182/blood-2013-08-519124. Epub 2013 Oct 1. Blood. 2013. PMID: 24085769 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Foster PA, Fulcher CA, Houghten RA, Zimmerman TS. A synthetic factor VIII peptide of eight amino acid residues (1677–1684) contains the binding region of an anti-factor VIII antibody which inhibits the binding of factor VIII to von Willebrand factor. Thromb Haemost. 1990;63:403–406. - PubMed
-
- Saenko EL, Scandella D. The acidic region of the factor VIII light chain and the C2 domain together form the high affinity binding site for von willebrand factor. J Biol Chem. 1997;272:18007–18014. - PubMed
-
- Rosing J, van Rijn JL, Bevers EM, van Dieijen G, Comfurius P, Zwaal RF. The role of activated human platelets in prothrombin and factor X activation. Blood. 1985;65:319–332. - PubMed
-
- Jurk K, Kehrel BE. Platelets: physiology and biochemistry. Semin Thromb Hemost. 2005;31:381–392. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

