Survivin repression by p53, Rb and E2F2 in normal human melanocytes
- PMID: 17916908
- PMCID: PMC2292458
- DOI: 10.1093/carcin/bgm219
Survivin repression by p53, Rb and E2F2 in normal human melanocytes
Abstract
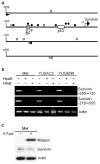
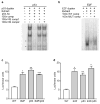
The inhibitor of apoptosis protein survivin is a dual mediator of apoptosis resistance and cell cycle progression and is highly expressed in cancer. We have shown previously that survivin is up-regulated in melanoma compared with normal melanocytes, is required for melanoma cell viability, and that melanocyte expression of survivin predisposes mice to ultraviolet-induced melanoma and metastasis. The mechanism of survivin up-regulation in the course of melanocyte transformation and its repression in normal melanocytes, however, has not been clearly defined. We show here that p53 and retinoblastoma (Rb), at basal levels and in the absence of any activating stimuli, are both required to repress survivin transcription in normal human melanocytes. Survivin repression in melanocytes does not involve alterations in protein stability or promoter methylation. p53 and Rb (via E2Fs) regulate survivin expression by direct binding to the survivin promoter; p53 also affects survivin expression by activating p21. We demonstrate a novel role for E2F2 in the negative regulation of survivin expression. In addition, we identify a novel E2F-binding site in the survivin promoter and show that mutation of either the p53- or E2F-binding sites is sufficient to increase promoter activity. These studies suggest that compromise of either p53 or Rb pathways during melanocyte transformation leads to up-regulation of survivin expression in melanoma.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Aberrant regulation of survivin by the RB/E2F family of proteins.J Biol Chem. 2004 Sep 24;279(39):40511-20. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M404496200. Epub 2004 Jul 22. J Biol Chem. 2004. PMID: 15271987
-
Transcriptional repression of the anti-apoptotic survivin gene by wild type p53.J Biol Chem. 2002 Feb 1;277(5):3247-57. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M106643200. Epub 2001 Nov 19. J Biol Chem. 2002. PMID: 11714700
-
Cell proliferation in the absence of E2F1-3.Dev Biol. 2011 Mar 1;351(1):35-45. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2010.12.025. Epub 2010 Dec 23. Dev Biol. 2011. PMID: 21185283 Free PMC article.
-
Rb/E2F: a two-edged sword in the melanocytic system.Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2005 Jun;24(2):339-56. doi: 10.1007/s10555-005-1582-z. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2005. PMID: 15986142 Review.
-
Melanoma cell autonomous growth: the Rb/E2F pathway.Cancer Metastasis Rev. 1999;18(3):333-43. doi: 10.1023/a:1006396104073. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 1999. PMID: 10721488 Review.
Cited by
-
Latency-associated nuclear antigen of Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus (KSHV) upregulates survivin expression in KSHV-Associated B-lymphoma cells and contributes to their proliferation.J Virol. 2009 Jul;83(14):7129-41. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00397-09. Epub 2009 May 13. J Virol. 2009. PMID: 19439469 Free PMC article.
-
Indirect p53-dependent transcriptional repression of Survivin, CDC25C, and PLK1 genes requires the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p21/CDKN1A and CDE/CHR promoter sites binding the DREAM complex.Oncotarget. 2015 Dec 8;6(39):41402-17. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.6356. Oncotarget. 2015. PMID: 26595675 Free PMC article.
-
Emerging Importance of Survivin in Stem Cells and Cancer: the Development of New Cancer Therapeutics.Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2020 Oct;16(5):828-852. doi: 10.1007/s12015-020-09995-4. Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2020. PMID: 32691369 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of E2F2 in cancer progression and its value as a therapeutic target.Front Immunol. 2024 May 14;15:1397303. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1397303. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38807594 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Single-cell analysis unveils cell subtypes of acral melanoma cells at the early and late differentiation stages.J Cancer. 2025 Jan 1;16(3):898-916. doi: 10.7150/jca.102045. eCollection 2025. J Cancer. 2025. PMID: 39781353 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Miller AJ, Mihm MC., Jr Melanoma. N Engl J Med. 2006;355:51–65. - PubMed
-
- Satyamoorthy K, Bogenrieder T, Herlyn M. No longer a molecular black box--new clues to apoptosis and drug resistance in melanoma. Trends Mol Med. 2001;7:191–194. - PubMed
-
- Omholt K, Platz A, Kanter L, Ringborg U, Hansson J. NRAS and BRAF mutations arise early during melanoma pathogenesis and are preserved throughout tumor progression. Clin Cancer Res. 2003;9:6483–6488. - PubMed
-
- Pirker C, Holzmann K, Spiegl-Kreinecker S, Elbling L, Thallinger C, Pehamberger H, Micksche M, Berger W. Chromosomal imbalances in primary and metastatic melanomas: over-representation of essential telomerase genes. Melanoma Res. 2003;13:483–492. - PubMed
-
- Sharpless E, Chin L. The INK4a/ARF locus and melanoma. Oncogene. 2003;22:3092–3098. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

