Longitudinal brain corticotropin releasing factor and somatostatin in a transgenic mouse (TG2576) model of Alzheimer's disease
- PMID: 17917156
- PMCID: PMC2919580
- DOI: 10.3233/jad-2007-12201
Longitudinal brain corticotropin releasing factor and somatostatin in a transgenic mouse (TG2576) model of Alzheimer's disease
Abstract
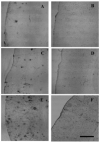
Neuropeptides corticotropin releasing factor (CRF) and somatostatin (SRIF) are substantially decreased in cortical regions of Alzheimer's disease (AD) post-mortem brain tissue. The accumulation of amyloid-beta (Abeta) in AD brain has been postulated to be neurotoxic. Using male Tg2576 mice transgenic over-expressing amyloid-beta protein precursor (APP), we examined brain concentrations of CRF and SRIF at 12, 18 and 24 months. Mice were evaluated for locomotor activity and spatial memory. The APP mice had continued increased locomotor activity from 6 months of age compared to controls. Spatial memory was impaired beginning at 12 months in the APP mice relative to controls. APP mice at 24 months had a significantly higher number of amyloid plaques when compared to the 12 and 18 month time points. Brain concentrations of SRIF and CRF were significantly altered in a number of cortical and sub-cortical brain regions relative to controls, but in most regions were increased rather than decreased as in clinical AD. This data shows that although the insertion of the APP gene does cause age dependent increase in plaque load, it does not cause a change in regional neuropeptides consistent with AD, suggesting that neuropeptide changes in AD are not solely due to Abeta load.
Figures
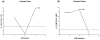

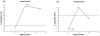

Similar articles
-
Amyloid-β plaque formation and reactive gliosis are required for induction of cognitive deficits in App knock-in mouse models of Alzheimer's disease.BMC Neurosci. 2019 Mar 20;20(1):13. doi: 10.1186/s12868-019-0496-6. BMC Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 30894120 Free PMC article.
-
β-Amyloid, cholinergic transmission, and cerebrovascular system -- a developmental study in a mouse model of Alzheimer's disease.Curr Pharm Des. 2013;19(38):6749-65. doi: 10.2174/13816128113199990711. Curr Pharm Des. 2013. PMID: 23530514
-
Effects of corticotrophin-releasing factor receptor 1 antagonists on amyloid-β and behavior in Tg2576 mice.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2014 Dec;231(24):4711-22. doi: 10.1007/s00213-014-3629-8. Epub 2014 May 27. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2014. PMID: 24862368 Free PMC article.
-
Corticotrophin releasing factor accelerates neuropathology and cognitive decline in a mouse model of Alzheimer's disease.J Alzheimers Dis. 2012;28(3):579-92. doi: 10.3233/JAD-2011-111328. J Alzheimers Dis. 2012. PMID: 22045495 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of CRFR1 Ablation on Amyloid-β Production and Accumulation in a Mouse Model of Alzheimer's Disease.J Alzheimers Dis. 2015;45(4):1175-84. doi: 10.3233/JAD-142844. J Alzheimers Dis. 2015. PMID: 25697705 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Stress-induced tau phosphorylation: functional neuroplasticity or neuronal vulnerability?J Alzheimers Dis. 2009;18(2):453-7. doi: 10.3233/JAD-2009-1153. J Alzheimers Dis. 2009. PMID: 19584431 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cross-sectional comparison of small animal [18F]-florbetaben amyloid-PET between transgenic AD mouse models.PLoS One. 2015 Feb 23;10(2):e0116678. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0116678. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25706990 Free PMC article.
-
Early-onset and robust amyloid pathology in a new homozygous mouse model of Alzheimer's disease.PLoS One. 2009 Nov 20;4(11):e7931. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0007931. PLoS One. 2009. PMID: 19936202 Free PMC article.
-
Social Isolation as a Risk Factor for Dementia: Insights from Animal Model Studies.Curr Alzheimer Res. 2025;22(3):165-173. doi: 10.2174/0115672050373522250421054927. Curr Alzheimer Res. 2025. PMID: 40296618 Review.
-
Effects of NK-4 in a transgenic mouse model of Alzheimer's disease.PLoS One. 2012;7(1):e30007. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0030007. Epub 2012 Jan 4. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22238689 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Barnes P, Good M. Impaired Pavlovian cued fear conditioning in Tg2576 mice expressing a human mutant amyloid precursor protein gene. Behav Brain Res. 2005 Feb.157(1):107–117. - PubMed
-
- Beal MF, Mazurek MF, Tran VT, Chatta G, Brid ED, Martin JB. Reduced numbers of somatostatin receptors in the cerebral cortex in Alzheimer's disease. Science. 1985;229:289–291. - PubMed
-
- Behan DP, Heinrichs SC, Troncoso JC, Liu XL, Kawas CH, Ling N, DeSouza EB. Displacement of Corticotropin-releasing factor from its binding protein as a possible treatment for Alzheimer's disease. Nature. 1995;378:284–287. - PubMed
-
- Bissette G, Reynolds GP, Kilts CD, Widerlov E, Nemeroff CB. Corticotrophin releasing factor-like immunoreactivity in senile dementia of Alzheimer's type. J Am Med Assoc. 1985;254:3067–3069. - PubMed
-
- Bissette G, Myers B. Minireview. Somatostatin in Alzheimer's disease and Depression. Life Sciences. 1992;51:1389–1410. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

