Antihypertensive efficacy of the oral direct renin inhibitor aliskiren as add-on therapy in patients not responding to amlodipine monotherapy
- PMID: 17917501
- PMCID: PMC8109853
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1524-6175.2007.06614.x
Antihypertensive efficacy of the oral direct renin inhibitor aliskiren as add-on therapy in patients not responding to amlodipine monotherapy
Abstract
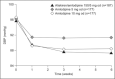
This study investigated the addition of the direct renin inhibitor aliskiren to amlodipine in patients with mild to moderate hypertension that was inadequately controlled with amlodipine alone. Following once-daily treatment with amlodipine 5 mg for 4 weeks, patients whose hypertension responded inadequately to therapy (mean sitting diastolic blood pressure [DBP] 90-109 mm Hg) (n=545) were randomized to 6 weeks of double-blind treatment with amlodipine 5 mg plus aliskiren 150 mg, amlodipine 5 mg, or amlodipine 10 mg. At the study's end, mean systolic blood pressure and DBP reductions with the combination of aliskiren 150 mg and amlodipine 5 mg (11.0/8.5 mm Hg) were significantly greater (P<.0001) than with amlodipine 5 mg (5.0/4.8 mm Hg)--the comparator group--but similar to amlodipine 10 mg (9.6/8.0 mm Hg). All treatments were well tolerated. Edema occurred more frequently with amlodipine 10 mg (11.2%) than with combination therapy (2.1%) or amlodipine 5 mg (3.4%). In conclusion, aliskiren 150 mg plus amlodipine 5 mg shows similar but not better blood pressure-lowering efficacy when compared with amlodipine 10 mg in patients not completely responsive to amlodipine 5 mg; less edema was noted with combination therapy.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Comparison of aliskiren/hydrochlorothiazide combination therapy and amlodipine monotherapy in patients with stage 2 systolic hypertension and type 2 diabetes mellitus.J Clin Hypertens (Greenwich). 2011 Dec;13(12):889-97. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-7176.2011.00552.x. Epub 2011 Nov 11. J Clin Hypertens (Greenwich). 2011. PMID: 22142348 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Efficacy and safety of aliskiren and amlodipine combination therapy in patients with hypertension: a randomized, double-blind, multifactorial study.J Hum Hypertens. 2013 May;27(5):321-7. doi: 10.1038/jhh.2012.42. Epub 2012 Oct 18. J Hum Hypertens. 2013. PMID: 23076450 Clinical Trial.
-
Direct Renin inhibition with aliskiren in obese patients with arterial hypertension.Hypertension. 2007 May;49(5):1047-55. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.106.084301. Epub 2007 Mar 12. Hypertension. 2007. PMID: 17353513 Clinical Trial.
-
Aliskiren: an oral renin inhibitor for the treatment of hypertension.Cardiol Rev. 2007 Nov-Dec;15(6):316-23. doi: 10.1097/CRD.0b013e31814852a4. Cardiol Rev. 2007. PMID: 18090068 Review.
-
The efficacy of aliskiren, a direct renin inhibitor, in the treatment of hypertension.Rev Cardiovasc Med. 2007;8 Suppl 2:S22-30. Rev Cardiovasc Med. 2007. PMID: 17401313 Review.
Cited by
-
Renin Inhibition with Aliskiren: A Decade of Clinical Experience.J Clin Med. 2017 Jun 9;6(6):61. doi: 10.3390/jcm6060061. J Clin Med. 2017. PMID: 28598381 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Oral renin inhibitors in clinical practice: a perspective review.Ther Adv Chronic Dis. 2012 Jul;3(4):173-81. doi: 10.1177/2040622312446244. Ther Adv Chronic Dis. 2012. PMID: 23342233 Free PMC article.
-
Application of direct renin inhibition to chronic kidney disease.Cardiovasc Drugs Ther. 2010 Apr;24(2):139-49. doi: 10.1007/s10557-010-6232-1. Cardiovasc Drugs Ther. 2010. PMID: 20490905 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Aliskiren, amlodipine and hydrochlorothiazide triple combination for hypertension.Expert Rev Cardiovasc Ther. 2012 Mar;10(3):293-303. doi: 10.1586/erc.12.7. Expert Rev Cardiovasc Ther. 2012. PMID: 22390800 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Aliskiren Inhibits Neointimal Matrix Metalloproteinases in Experimental Atherosclerosis.Acta Cardiol Sin. 2016 Sep;32(5):586-593. doi: 10.6515/acs20151012c. Acta Cardiol Sin. 2016. PMID: 27713608 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Seventh Report of the Joint National Committee on Prevention, Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Pressure. Hypertension. 2003;42(6):1206–1252. - PubMed
-
- European Society of Hypertension‐European Society of Cardiology . 2003 European Society of Hypertension‐European Society of Cardiology guidelines for the management of arterial hypertension. J Hypertens. 2003;21(6):1011–1053. - PubMed
-
- Hansson L, Zanchetti A, Carruthers SG, et al. Effects of intensive blood‐pressure lowering and low‐dose aspirin in patients with hypertension: principal results of the Hypertension Optimal Treatment (HOT) randomised trial. HOT Study Group . Lancet. 1998;351(9118):1755–1762. - PubMed
-
- Wang YR, Alexander GC, Stafford RS. Outpatient hypertension treatment, treatment intensification, and control in Western Europe and the United States. Arch Intern Med. 2007;167: 141–147. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

