Tel1 kinase and subtelomere-bound Tbf1 mediate preferential elongation of short telomeres by telomerase in yeast
- PMID: 17917674
- PMCID: PMC2247385
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.embor.7401082
Tel1 kinase and subtelomere-bound Tbf1 mediate preferential elongation of short telomeres by telomerase in yeast
Abstract
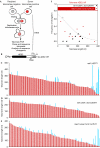
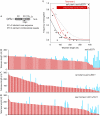
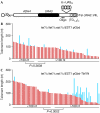
Telomerase enables telomere length homeostasis, exhibiting increasing preference for telomeres as their lengths decline. This regulation involves telomere repeat-bound Rap1, which provides a length-dependent negative feedback mechanism, and the Tel1 and Mec1 kinases, which are positive regulators of telomere length. By analysing telomere elongation of wild-type chromosome ends at single-molecule resolution, we show that in tel1Delta cells the overall frequency of elongation decreases considerably, explaining their short telomere phenotype. At an artificial telomere lacking a subtelomeric region, telomere elongation no longer increases with telomere shortening in tel1Delta cells. By contrast, a natural telomere, containing subtelomeric sequence, retains a preference for the elongation of short telomeres. Tethering of the subtelomere binding protein Tbf1 to the artificial telomere in tel1Delta cells restored preferential telomerase action at short telomeres; thus, Tbf1 might function in parallel to Tel1, which has a crucial role in a TG-repeat-controlled pathway for the activation of telomerase at short telomeres.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Subtelomere-binding protein Tbf1 and telomere-binding protein Rap1 collaborate to inhibit localization of the Mre11 complex to DNA ends in budding yeast.Mol Biol Cell. 2012 Jan;23(2):347-59. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E11-06-0568. Epub 2011 Nov 30. Mol Biol Cell. 2012. PMID: 22130795 Free PMC article.
-
Subtelomeric proteins negatively regulate telomere elongation in budding yeast.EMBO J. 2006 Feb 22;25(4):846-56. doi: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7600975. Epub 2006 Feb 9. EMBO J. 2006. PMID: 16467854 Free PMC article.
-
Altering telomere structure allows telomerase to act in yeast lacking ATM kinases.Curr Biol. 2001 Aug 21;11(16):1240-50. doi: 10.1016/s0960-9822(01)00391-8. Curr Biol. 2001. PMID: 11525738
-
Telomere length homeostasis.Chromosoma. 2006 Dec;115(6):413-25. doi: 10.1007/s00412-006-0067-3. Epub 2006 Jun 2. Chromosoma. 2006. PMID: 16741708 Review.
-
Telomere length regulation: coupling DNA end processing to feedback regulation of telomerase.EMBO J. 2009 Aug 19;28(16):2309-22. doi: 10.1038/emboj.2009.195. Epub 2009 Jul 23. EMBO J. 2009. PMID: 19629031 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
ATR cooperates with CTC1 and STN1 to maintain telomeres and genome integrity in Arabidopsis.Mol Biol Cell. 2012 Apr;23(8):1558-68. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E11-12-1002. Epub 2012 Feb 22. Mol Biol Cell. 2012. PMID: 22357613 Free PMC article.
-
Tbf1 and Vid22 promote resection and non-homologous end joining of DNA double-strand break ends.EMBO J. 2013 Jan 23;32(2):275-89. doi: 10.1038/emboj.2012.327. Epub 2012 Dec 7. EMBO J. 2013. PMID: 23222485 Free PMC article.
-
Telomere length homeostasis responds to changes in intracellular dNTP pools.Genetics. 2013 Apr;193(4):1095-105. doi: 10.1534/genetics.112.149120. Epub 2013 Jan 18. Genetics. 2013. PMID: 23335335 Free PMC article.
-
Novel connections between DNA replication, telomere homeostasis, and the DNA damage response revealed by a genome-wide screen for TEL1/ATM interactions in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Genetics. 2013 Apr;193(4):1117-33. doi: 10.1534/genetics.113.149849. Epub 2013 Feb 1. Genetics. 2013. PMID: 23378069 Free PMC article.
-
Length-dependent processing of telomeres in the absence of telomerase.Nucleic Acids Res. 2014 Apr;42(6):3648-65. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkt1328. Epub 2014 Jan 6. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014. PMID: 24393774 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chan SW, Chang J, Prescott J, Blackburn EH (2001) Altering telomere structure allows telomerase to act in yeast lacking ATM kinases. Curr Biol 11: 1240–1250 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

