The carboxy-terminal coiled-coil of the RNA polymerase beta'-subunit is the main binding site for Gre factors
- PMID: 17917675
- PMCID: PMC2247394
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.embor.7401079
The carboxy-terminal coiled-coil of the RNA polymerase beta'-subunit is the main binding site for Gre factors
Abstract
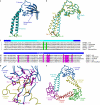
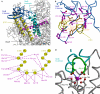
Bacterial Gre transcript cleavage factors stimulate the intrinsic endonucleolytic activity of RNA polymerase (RNAP) to rescue stalled transcription complexes. They bind to RNAP and extend their coiled-coil (CC) domains to the catalytic centre through the secondary channel. Three existing models for the Gre-RNAP complex postulate congruent mechanisms of Gre-assisted catalysis, while offering conflicting views of the Gre-RNAP interactions. Here, we report the GreB structure of Escherichia coli. The GreB monomers form a triangle with the tip of the amino-terminal CC of one molecule trapped within the hydrophobic cavity of the carboxy-terminal domain of a second molecule. This arrangement suggests an analogous model for recruitment to RNAP. Indeed, the beta'-subunit CC located at the rim of the secondary channel has conserved hydrophobic residues at its tip. We show that substitutions of these residues and those in the GreB C-terminal domain cavity confer defects in GreB activity and binding to RNAP, and present a plausible model for the RNAP-GreB complex.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Transcript cleavage factors GreA and GreB act as transient catalytic components of RNA polymerase.EMBO J. 2003 Dec 1;22(23):6322-34. doi: 10.1093/emboj/cdg610. EMBO J. 2003. PMID: 14633991 Free PMC article.
-
An insertion in the catalytic trigger loop gates the secondary channel of RNA polymerase.J Mol Biol. 2013 Jan 9;425(1):82-93. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2012.11.008. Epub 2012 Nov 9. J Mol Biol. 2013. PMID: 23147217 Free PMC article.
-
Dynamics of GreB-RNA polymerase interaction allow a proofreading accessory protein to patrol for transcription complexes needing rescue.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2017 Feb 14;114(7):E1081-E1090. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1616525114. Epub 2017 Jan 30. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2017. PMID: 28137878 Free PMC article.
-
Conformational toggle triggers a modulator of RNA polymerase activity.Trends Biochem Sci. 2006 Aug;31(8):424-6. doi: 10.1016/j.tibs.2006.06.004. Epub 2006 Jul 11. Trends Biochem Sci. 2006. PMID: 16815708 Review.
-
A Two-Way Street: Regulatory Interplay between RNA Polymerase and Nascent RNA Structure.Trends Biochem Sci. 2016 Apr;41(4):293-310. doi: 10.1016/j.tibs.2015.12.009. Epub 2016 Jan 25. Trends Biochem Sci. 2016. PMID: 26822487 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
High-mobility-group a-like CarD binds to a DNA site optimized for affinity and position and to RNA polymerase to regulate a light-inducible promoter in Myxococcus xanthus.J Bacteriol. 2013 Jan;195(2):378-88. doi: 10.1128/JB.01766-12. Epub 2012 Nov 9. J Bacteriol. 2013. PMID: 23144251 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Histone Tails and Single Strand DNA Breaks in Nucleosomal Arrest of RNA Polymerase.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jan 24;24(3):2295. doi: 10.3390/ijms24032295. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36768621 Free PMC article.
-
In silico discovery of small molecules that inhibit RfaH recruitment to RNA polymerase.Mol Microbiol. 2018 Oct;110(1):128-142. doi: 10.1111/mmi.14093. Epub 2018 Oct 2. Mol Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 30069925 Free PMC article.
-
RNA polymerase pausing, stalling and bypass during transcription of damaged DNA: from molecular basis to functional consequences.Nucleic Acids Res. 2022 Apr 8;50(6):3018-3041. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkac174. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022. PMID: 35323981 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bacterial Transcription as a Target for Antibacterial Drug Development.Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2016 Jan 13;80(1):139-60. doi: 10.1128/MMBR.00055-15. Print 2016 Mar. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2016. PMID: 26764017 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Artsimovitch I, Chu C, Lynch AS, Landick R (2003) A new class of bacterial RNA polymerase inhibitor affects nucleotide addition. Science 302: 650–654 - PubMed
-
- Borukhov S, Sagitov V, Goldfarb A (1993) Transcript cleavage factors from E. coli. Cell 72: 459–466 - PubMed
-
- Bryant GO, Martel LS, Burley SK, Berk AJ (1996) Radical mutations reveal TATA-box binding protein surfaces required for activated transcription in vivo. Genes Dev 10: 2491–2504 - PubMed
-
- Erie DA, Hajiseyedjavadi O, Young MC, von Hippel PH (1993) Multiple RNA polymerase conformations and GreA: control of the fidelity of transcription. Science 262: 867–873 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

