From docking false-positive to active anti-HIV agent
- PMID: 17918923
- PMCID: PMC2575345
- DOI: 10.1021/jm070683u
From docking false-positive to active anti-HIV agent
Abstract
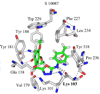
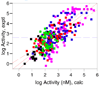
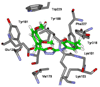
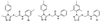
Virtual screening of the Maybridge library of ca. 70 000 compounds was performed using a similarity filter, docking, and molecular mechanics-generalized Born/surface area postprocessing to seek potential non-nucleoside inhibitors of human immunodeficiency virus-1 (HIV-1) reverse transcriptase (NNRTIs). Although known NNRTIs were retrieved well, purchase and assaying of representative, top-scoring compounds from the library failed to yield any active anti-HIV agents. However, the highest-ranked library compound, oxadiazole 1, was pursued as a potential "near-miss" with the BOMB program to seek constructive modifications. Subsequent synthesis and assaying of several polychloro-analogs did yield anti-HIV agents with EC50 values as low as 310 nM. The study demonstrates that it is possible to learn from a formally unsuccessful virtual-screening exercise and, with the aid of computational analyses, to efficiently evolve a false positive into a true active.
Figures
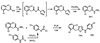
Similar articles
-
Search for non-nucleoside inhibitors of HIV-1 reverse transcriptase using chemical similarity, molecular docking, and MM-GB/SA scoring.J Chem Inf Model. 2007 Nov-Dec;47(6):2416-28. doi: 10.1021/ci700271z. Epub 2007 Oct 20. J Chem Inf Model. 2007. PMID: 17949071 Free PMC article.
-
Development of nonnucleoside HIV reverse transcriptase inhibitors.Methods Enzymol. 1996;275:440-72. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(96)75026-7. Methods Enzymol. 1996. PMID: 9026654 Review. No abstract available.
-
Design, synthesis, and anti-HIV-1 activity of 1-aromatic methyl-substituted 3-(3,5-dimethylbenzyl)uracil and N-3,5-dimethylbenzyl-substituted urea derivatives.Antivir Chem Chemother. 2015 Feb;24(1):3-18. doi: 10.1177/2040206614566584. Antivir Chem Chemother. 2015. PMID: 26149262 Free PMC article.
-
Design, synthesis and biological evaluation of quinoxaline compounds as anti-HIV agents targeting reverse transcriptase enzyme.Eur J Med Chem. 2020 Feb 15;188:111987. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2019.111987. Epub 2019 Dec 23. Eur J Med Chem. 2020. PMID: 31893549
-
Focus on Chirality of HIV-1 Non-Nucleoside Reverse Transcriptase Inhibitors.Molecules. 2016 Feb 16;21(2):221. doi: 10.3390/molecules21020221. Molecules. 2016. PMID: 26891289 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Computational drug design strategies applied to the modelling of human immunodeficiency virus-1 reverse transcriptase inhibitors.Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz. 2015 Nov;110(7):847-64. doi: 10.1590/0074-02760150239. Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz. 2015. PMID: 26560977 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A molecular evolution algorithm for ligand design in DOCK.J Comput Chem. 2022 Nov 5;43(29):1942-1963. doi: 10.1002/jcc.26993. Epub 2022 Sep 8. J Comput Chem. 2022. PMID: 36073674 Free PMC article.
-
Efficient drug lead discovery and optimization.Acc Chem Res. 2009 Jun 16;42(6):724-33. doi: 10.1021/ar800236t. Acc Chem Res. 2009. PMID: 19317443 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prediction of the water content in protein binding sites.J Phys Chem B. 2009 Oct 8;113(40):13337-46. doi: 10.1021/jp9047456. J Phys Chem B. 2009. PMID: 19754086 Free PMC article.
-
Discovery of novel fibroblast growth factor receptor 1 kinase inhibitors by structure-based virtual screening.J Med Chem. 2010 Feb 25;53(4):1662-72. doi: 10.1021/jm901386e. J Med Chem. 2010. PMID: 20121196 Free PMC article.
References
-
- 2006 AIDS Epidemic Update. Geneva: UNAIDS; 2006.
-
- Kohlstaedt LA, Wang J, Friedman JM, Rice PA, Steitz TA. Crystal structure at 3.5 Å resolution of HIV-1 reverse transcriptase complexed with an inhibitor. Science. 1992;256:1783–1790. - PubMed
- Smerdon SJ, Jäger J, Wang J, Kohlstaedt LA, Chirino AJ, Friedman JM, Rice PA, Steitz TA. Structure of the binding site for nonnucleoside inhibitors of reverse transcriptase of human immunodeficiency virus type 1. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 1994;91:3911–3915. - PMC - PubMed
- De Clercq E. New approaches toward anti-HIV chemotherapy. J. Med. Chem. 2005;48:1297–1313. - PubMed
-
- Jorgensen WL, Ruiz-Caro J, Tirado-Rives J, Basavapathruni A, Anderson KS, Hamilton AD. Computer-aided design of non-nucleoside inhibitors of HIV-1 reverse transcriptase. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2006;16:663–667. - PubMed
- Ruiz-Caro J, Basavapathruni A, Kim JT, Wang L, Bailey CM, Anderson KS, Hamilton AD, Jorgensen WL. Optimization of diarylamines as non-nucleoside inhibitors of HIV-1 reverse transcriptase. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2006;16:668–671. - PubMed
- Thakur VV, Kim JT, Hamilton AD, Bailey CM, Domaoal RA, Wang L, Anderson KS, Jorgensen WL. Optimization of pyrimidinyl- and triazinyl-amines as non-nucleoside inhibitors of HIV-1 reverse transcriptase. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2006;16:5664–5667. - PubMed
- Kim JT, Hamilton AD, Bailey CM, Domaoal RA, Wang L, Anderson KS, Jorgensen WL. FEP-guided selection of bicyclic heterocycles in lead optimization for non-nucleoside inhibitors of HIV-1 reverse transcriptase. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006;128:15372–15373. - PubMed
-
- Blake JF, Laird ER. Recent advances in virtual ligand screening. Ann. Rep. Med. Chem. 2003;38:305–314.
- Leach AR, Shoichet BK, Peishoff CE. Prediction of protein-ligand interactions. Docking and scoring: successes and gaps. J. Med. Chem. 2006;49:5851–5855. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

