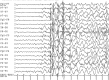
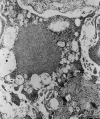
A 12-year-old girl with seizures and dementia
- PMID: 17919132
- PMCID: PMC8095514
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1750-3639.2007.00091_2.x
A 12-year-old girl with seizures and dementia
Similar articles
-
[Progressive myoclonic epilepsy type Lafora].J Med Liban. 2001 May-Jun;49(3):170-2. J Med Liban. 2001. PMID: 12187920 French.
-
[Lafora disease: histopathological study of axillary cutaneous biopsy].Ann Pathol. 2013 Apr;33(2):84-6. doi: 10.1016/j.annpat.2013.02.002. Epub 2013 Mar 26. Ann Pathol. 2013. PMID: 23582833 French.
-
[Lafora disease. A new case of confirmation of diagnosis on molecular genetic studies].Rev Neurol. 2002 Jan 16-31;34(2):117-20. Rev Neurol. 2002. PMID: 11988905 Spanish.
-
Progressive myoclonus epilepsy with polyglucosan bodies: Lafora disease.Adv Neurol. 2002;89:199-210. Adv Neurol. 2002. PMID: 11968446 Review. No abstract available.
-
Advances in lafora progressive myoclonus epilepsy.Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep. 2007 Sep;7(5):428-33. doi: 10.1007/s11910-007-0066-7. Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep. 2007. PMID: 17764634 Review.
Cited by
-
Structural and Functional Brain Abnormalities in Mouse Models of Lafora Disease.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Oct 20;21(20):7771. doi: 10.3390/ijms21207771. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33092303 Free PMC article.
-
MRI characteristics due to gene mutations in a Chinese pedigree with Lafora disease.Mol Genet Genomic Med. 2023 Oct;11(10):e2228. doi: 10.1002/mgg3.2228. Epub 2023 Jul 17. Mol Genet Genomic Med. 2023. PMID: 37455597 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Andrade DM, Ackerley CA, Minett TS et al (2003) Skin biopsy in Lafora disease: genotype‐phenotype correlations and diagnostic pitfalls. Neurology 61:1611–1614. - PubMed
-
- Annesi G, Sofia V, Gambardella A et al (2004) A novel exon 1 mutation in a patient with atypical lafora progressive myoclonus epilepsy seen as childhood‐onset cognitive deficit. Epilepsia 45:294–295. - PubMed
-
- Chan EM, Young EJ, Ianzano L et al (2003) Mutations in NHLRC1 cause progressive myoclonus epilepsy. Nat Genet 35:125–127. - PubMed
-
- Ellison D, Love S, Chimelli L et al (2000) Miscellaneous pediatric disorders. In: Neuropathology. Ellison D, Love S (ed.), pp. 149–157. Mosby: London.
-
- Fernandez‐Sanchez ME, Criado‐Garcia O, Heath KE et al (2003) Laforin, the dual‐phosphatase responsible for Lafora disease, interacts with R5 (PTG), a regulatory subunit of protein phosphatase‐1 that enhances glycogen accumulation. Hum Mol Genet 12:3161–3171. - PubMed