Action potentials and insulin secretion: new insights into the role of Kv channels
- PMID: 17919183
- PMCID: PMC5878925
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1463-1326.2007.00784.x
Action potentials and insulin secretion: new insights into the role of Kv channels
Abstract
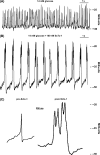
Coordinated electrical activity allows pancreatic beta-cells to respond to secretagogues with calcium entry followed by insulin secretion. Metabolism of glucose affects multiple membrane proteins including ion channels, transporters and pumps that collaborate in a cascade of electrical activity resulting in insulin release. Glucose induces beta-cell depolarization resulting in the firing of action potentials (APs), which are the primary electrical signal of the beta-cell. They are shaped by orchestrated activation of ion channels. Here we give an overview of the voltage-gated potassium (Kv) channels of the beta-cell, which are responsible in part for the falling phase of the AP, and how their regulation affects insulin secretion. beta cells contain several Kv channels allowing dynamic integration of multiple signals on repolarization of glucose-stimulated APs. Recent studies on Kv channel regulation by cAMP and arachidonic acid and on the Kv2.1 null mouse have greatly increased our understanding of beta-cell excitation-secretion coupling.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
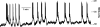
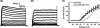
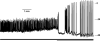
Similar articles
-
Voltage-dependent K(+) channels in pancreatic beta cells: role, regulation and potential as therapeutic targets.Diabetologia. 2003 Aug;46(8):1046-62. doi: 10.1007/s00125-003-1159-8. Epub 2003 Jun 27. Diabetologia. 2003. PMID: 12830383 Review.
-
Ion channels and the molecular control of insulin secretion.Biochem Soc Trans. 1994 Feb;22(1):6-12. doi: 10.1042/bst0220006. Biochem Soc Trans. 1994. PMID: 7515832 Review. No abstract available.
-
Inhibition of Kv2.1 voltage-dependent K+ channels in pancreatic beta-cells enhances glucose-dependent insulin secretion.J Biol Chem. 2002 Nov 22;277(47):44938-45. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M205532200. Epub 2002 Sep 20. J Biol Chem. 2002. PMID: 12270920
-
Ion channels, electrical activity and insulin secretion.Diabete Metab. 1994 Mar-Apr;20(2):138-45. Diabete Metab. 1994. PMID: 7528694 Review.
-
Ion channels and insulin secretion.Diabetes Care. 1990 Mar;13(3):340-63. doi: 10.2337/diacare.13.3.340. Diabetes Care. 1990. PMID: 1689632 Review.
Cited by
-
Pharmacological stimulation and inhibition of insulin secretion in mouse islets lacking ATP-sensitive K+ channels.Br J Pharmacol. 2010 Feb 1;159(3):669-77. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2009.00588.x. Epub 2010 Jan 28. Br J Pharmacol. 2010. PMID: 20128805 Free PMC article.
-
D2-Like Receptors Mediate Dopamine-Inhibited Insulin Secretion via Ion Channels in Rat Pancreatic β-Cells.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2020 Apr 7;11:152. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2020.00152. eCollection 2020. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2020. PMID: 32318020 Free PMC article.
-
A model of action potentials and fast Ca2+ dynamics in pancreatic beta-cells.Biophys J. 2009 Apr 22;96(8):3126-39. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2009.01.029. Biophys J. 2009. PMID: 19383458 Free PMC article.
-
Simplified method to isolate highly pure canine pancreatic islets.Pancreas. 2012 Jan;41(1):31-8. doi: 10.1097/MPA.0b013e318221fd0e. Pancreas. 2012. PMID: 21792087 Free PMC article.
-
Concerted Trafficking Regulation of Kv2.1 and KATP Channels by Leptin in Pancreatic β-Cells.J Biol Chem. 2015 Dec 11;290(50):29676-90. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M115.670877. Epub 2015 Oct 9. J Biol Chem. 2015. PMID: 26453299 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Dean PM, Matthews EK. Electrical activity on pancreatic islet cells. Nature. 1968;219:389–390. - PubMed
-
- Ashcroft FM, Rorsman P. Electrophysiology of the pancreatic beta-cell. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 1989;54:87–143. - PubMed
-
- Cook DL, Hales CN. Intracellular ATP directly blocks K+ channels in pancreatic B-cells. Nature. 1984;311:271–273. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

