Regulation of extracellular matrix remodeling and cell fate determination by matrix metalloproteinase stromelysin-3 during thyroid hormone-dependent post-embryonic development
- PMID: 17919732
- PMCID: PMC2754841
- DOI: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2007.07.005
Regulation of extracellular matrix remodeling and cell fate determination by matrix metalloproteinase stromelysin-3 during thyroid hormone-dependent post-embryonic development
Abstract
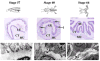
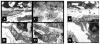
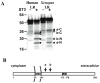
Interactions between cells and extracellular matrix (ECM), in particular the basement membrane (BM), are fundamentally important for the regulation of a wide variety of physiological and pathological processes. Matrix metalloproteinases (MMP) play critical roles in ECM remodeling and/or regulation of cell-ECM interactions because of their ability to cleave protein components of the ECM. Of particular interest among MMP is stromelysin-3 (ST3), which was first isolated from a human breast cancer and also shown to be correlated with apoptosis during development and invasion of tumor cells in mammals. We have been using intestinal remodeling during thyroid hormone (TH)-dependent amphibian metamorphosis as a model to study the role of ST3 during post-embryonic tissue remodeling and organ development in vertebrates. This process involves complete degeneration of the tadpole or larval epithelium through apoptosis and de novo development of the adult epithelium. Here, we will first summarize expression studies by us and others showing a tight spatial and temporal correlation of the expression of ST3 mRNA and protein with larval cell death and adult tissue development. We will then review in vitro and in vivo data supporting a critical role of ST3 in TH-induced larval epithelial cell death and ECM remodeling. We will further discuss the potential mechanisms of ST3 function during metamorphosis and its broader implications.
Figures

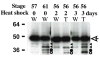

Similar articles
-
A causative role of stromelysin-3 in extracellular matrix remodeling and epithelial apoptosis during intestinal metamorphosis in Xenopus laevis.J Biol Chem. 2005 Jul 29;280(30):27856-65. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M413275200. Epub 2005 Jun 1. J Biol Chem. 2005. PMID: 15929979
-
Tissue-dependent induction of apoptosis by matrix metalloproteinase stromelysin-3 during amphibian metamorphosis.Birth Defects Res C Embryo Today. 2010 Mar;90(1):55-66. doi: 10.1002/bdrc.20170. Birth Defects Res C Embryo Today. 2010. PMID: 20301218 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Requirement for matrix metalloproteinase stromelysin-3 in cell migration and apoptosis during tissue remodeling in Xenopus laevis.J Cell Biol. 2000 Sep 4;150(5):1177-88. doi: 10.1083/jcb.150.5.1177. J Cell Biol. 2000. PMID: 10974004 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptional activation of the matrix metalloproteinase gene stromelysin-3 coincides with thyroid hormone-induced cell death during frog metamorphosis.Dev Biol. 1995 Jan;167(1):252-62. doi: 10.1006/dbio.1995.1021. Dev Biol. 1995. PMID: 7851646
-
Thyroid hormone regulation of Xenopus laevis metamorphosis: functions of thyroid hormone receptors and roles of extracellular matrix remodeling.Wound Repair Regen. 1998 Jul-Aug;6(4):314-22. doi: 10.1046/j.1524-475x.1998.60407.x. Wound Repair Regen. 1998. PMID: 9824550 Review.
Cited by
-
Proteome of larval metamorphosis induced by epinephrine in the Fujian oyster Crassostrea angulata.BMC Genomics. 2020 Sep 29;21(1):675. doi: 10.1186/s12864-020-07066-z. BMC Genomics. 2020. PMID: 32993483 Free PMC article.
-
Comprehensive and Quantitative Proteomic Analysis of Metamorphosis-Related Proteins in the Veined Rapa Whelk, Rapana venosa.Int J Mol Sci. 2016 Jun 15;17(6):924. doi: 10.3390/ijms17060924. Int J Mol Sci. 2016. PMID: 27314339 Free PMC article.
-
Dysregulation of the MMP/TIMP Proteolytic System in Subependymal Giant Cell Astrocytomas in Patients With Tuberous Sclerosis Complex: Modulation of MMP by MicroRNA-320d In Vitro.J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 2020 Jul 1;79(7):777-790. doi: 10.1093/jnen/nlaa040. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 2020. PMID: 32472129 Free PMC article.
-
Matrix metalloproteinase 2 (MMP2) inhibition: DFT and QM/MM studies of the deprotonation-initialized ring-opening reaction of the sulfoxide analogue of SB-3CT.J Phys Chem B. 2010 Jan 21;114(2):1030-7. doi: 10.1021/jp909327y. J Phys Chem B. 2010. PMID: 20039633 Free PMC article.
-
Stage-dependent cardiac regeneration in Xenopus is regulated by thyroid hormone availability.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2019 Feb 26;116(9):3614-3623. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1803794116. Epub 2019 Feb 12. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2019. PMID: 30755533 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alexander CM, Werb Z. Extracellular matrix degradation. In: Hay ED, editor. Cell Biology of Extracellular Matrix. New York: Plenum Press; 1991. pp. 255–302.
-
- Alexander CM, Hansell EJ, Behrendtsen O, Flannery ML, Kishnani NS, Hawkes SP, Werb Z. Expression and function of matrix metalloproteinases and their inhibitors at the maternal-embryonic boundary durng mouse embryo implantation. Development. 1996;122:1723–1736. - PubMed
-
- Amano T, Noro N, Kawabata H, Kobayashi Y, Yoshizato K. Metamorphosis-associated and region-specific expression of calbindin gene in the posterior intestinal epithelium of Xenopus laevis larva. Dev Growth Differ. 1998;40:177–88. - PubMed
-
- Amano T, Fu L, Sahu S, Markey M, Shi YB. Substrate specificity of Xenopus matrix metalloproteinase stromelysin-3. International Journal of Molecular Medicine. 2004;14:233–239. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

