Evaluation of corticospinal axon loss by fluorescent dye tracing in mice with experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis
- PMID: 17919735
- PMCID: PMC2265634
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jneumeth.2007.08.013
Evaluation of corticospinal axon loss by fluorescent dye tracing in mice with experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis
Abstract
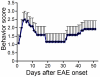
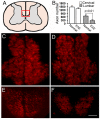
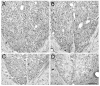
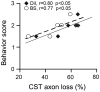
In both multiple sclerosis (MS) patients and experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE) animals, axon loss has been demonstrated to correlate with neurological disability. However, it is difficult to accurately determine the location and severity of axonal damage since the lesion in MS or EAE is disseminated and is frequently in a relapsing-remitting mode. The corticospinal system is the only direct pathway from the motorsensory cortex to the spinal cord, and the major neural pathway for control of voluntary movement. Moreover, it is frequently involved in the pathological process of the disease. To evaluate corticospinal tract (CST) axon loss in EAE mice, we developed a direct tracing method with a fluorescent neuronal tracer DiI which was injected into the primary motor cortex and sensorimotor cortex to label the pyramidal neurons. The lesion location in the spinal cord and axon disruption were indicated by dye leakage. Using the EAE induced axon reduction as an index of the extent of axonal damage, our data showed a high correlation between the axonal loss and the behavioral outcome score in the EAE mice. The results were consistent with the axonal Bielschowsky silver staining. Thus, this CST tracing method permits monitoring of the axonal damage in EAE.
Figures


References
-
- Arnold DL. Magnetic resonance spectroscopy: imaging axonal damage in MS. J Neuroimmunol. 1999;98:2–6. - PubMed
-
- Bechtold DA, Miller SJ, Dawson AC, Sun Y, Kapoor R, Berry D, Smith KJ. Axonal protection achieved in a model of multiple sclerosis using lamotrigine. J Neurol. 2006;253:1542–51. - PubMed
-
- Bettelli E. Building different mouse models for human MS. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2007;1103:11–8. - PubMed
-
- Bjartmar C, Kidd G, Mork S, Rudick R, Trapp BD. Neurological disability correlates with spinal cord axonal loss and reduced N-acetyl aspartate in chronic multiple sclerosis patients. Ann Neurol. 2000;48:893–901. - PubMed
-
- Bjartmar C, Wujek JR, Trapp BD. Axonal loss in the pathology of MS: consequences for understanding the progressive phase of the disease. J Neurol Sci. 2003;206:165–71. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

