Taking it step by step: mechanistic insights from structural studies of ubiquitin/ubiquitin-like protein modification pathways
- PMID: 17919899
- PMCID: PMC2174906
- DOI: 10.1016/j.sbi.2007.08.018
Taking it step by step: mechanistic insights from structural studies of ubiquitin/ubiquitin-like protein modification pathways
Abstract
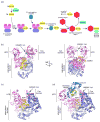
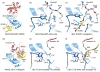
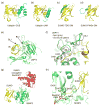
Ubiquitin (Ub) and ubiquitin-like (Ubl) proteins regulate a diverse array of cellular pathways through post-translational attachment to protein substrates. Ub/Ubl-mediated signaling is initiated through E1, E2, and E3-mediated conjugation, transduced by proteins that recognize Ub/Ubl-modified substrates, and terminated by proteases which remove the Ub/Ubl from the substrate. Recent structural studies have elucidated mechanisms pertinent to Ub/Ubl conjugation, recognition, and deconjugation, highlighting essential steps during Ub/Ubl modification that illustrate common and divergent mechanistic themes within this important process.
Figures

References
-
- Kerscher O, Felberbaum R, Hochstrasser M. Modification of proteins by ubiquitin and ubiquitin-like proteins. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2006;22:159–180. - PubMed
-
- Hershko A, Ciechanover A. The ubiquitin system. Annu Rev Biochem. 1998;67:425–479. - PubMed
-
- Walden H, Podgorski MS, Schulman BA. Insights into the ubiquitin transfer cascade from the structure of the activating enzyme for NEDD8. Nature. 2003;422:330–334. - PubMed
-
- Walden H, Podgorski MS, Huang DT, Miller DW, Howard RJ, Minor DL, Jr, Holton JM, Schulman BA. The structure of the APPBP1-UBA3-NEDD8-ATP complex reveals the basis for selective ubiquitin-like protein activation by an E1. Mol Cell. 2003;12:1427–1437. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

