Interleukin-22 but not interleukin-17 provides protection to hepatocytes during acute liver inflammation
- PMID: 17919941
- PMCID: PMC2149911
- DOI: 10.1016/j.immuni.2007.07.023
Interleukin-22 but not interleukin-17 provides protection to hepatocytes during acute liver inflammation
Abstract
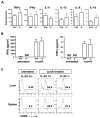
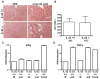
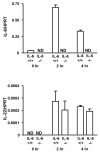
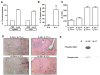
The cytokine interleukin-22 (IL-22) is primarily expressed by T helper 17 (Th17) CD4(+) T cells and is highly upregulated during chronic inflammatory diseases. IL-22 receptor expression is absent on immune cells, but is instead restricted to the tissues, providing signaling directionality from the immune system to the tissues. However, the role of IL-22 in inflammatory responses has been confounded by data suggesting both pro- and anti-inflammatory functions. Herein, we provide evidence that during inflammation, IL-22 played a protective role in preventing tissue injury. Hepatocytes from mice deficient in IL-22 were highly sensitive to the detrimental immune response associated with hepatitis. Additionally, IL-22-expressing Th17 cells provided protection during hepatitis in IL-22-deficient mice. On the other hand, interleukin-17 (IL-17), which is coexpressed with IL-22 and can induce similar cellular responses, had no observable role in liver inflammation. Our data suggest that IL-22 serves as a protective molecule to counteract the destructive nature of the immune response to limit tissue damage.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest
LAZ and RAF declare no conflict of interest. GDY, DMV, AJM and MK were employees of Regeneron Pharmaceuticals at the time this work was performed.
Figures
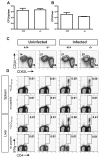
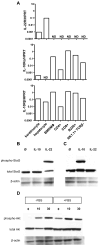
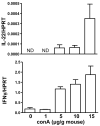
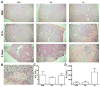
Comment in
-
Interleukin-22, interleukin-17, and other cytokines: a wall is coming down.Hepatology. 2008 Jan;47(1):345-8. doi: 10.1002/hep.22154. Hepatology. 2008. PMID: 18161709 No abstract available.
References
-
- Aggarwal S, Xie MH, Maruoka M, Foster J, Gurney AL. Acinar cells of the pancreas are a target of interleukin-22. J Interferon Cytokine Res. 2001;21:1047–1053. - PubMed
-
- Andoh A, Zhang Z, Inatomi O, Fujino S, Deguchi Y, Araki Y, Tsujikawa T, Kitoh K, Kim-Mitsuyama S, Takayanagi A, et al. Interleukin-22, a member of the IL-10 subfamily, induces inflammatory responses in colonic subepithelial myofibroblasts. Gastroenterology. 2005;129:969–984. - PubMed
-
- Bettelli E, Carrier Y, Gao W, Korn T, Strom TB, Oukka M, Weiner HL, Kuchroo VK. Reciprocal developmental pathways for the generation of pathogenic effector TH17 and regulatory T cells. Nature. 2006;441:235–238. - PubMed
-
- Boniface K, Bernard FX, Garcia M, Gurney AL, Lecron JC, Morel F. IL-22 inhibits epidermal differentiation and induces proinflammatory gene expression and migration of human keratinocytes. J Immunol. 2005;174:3695–3702. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

