MeCP2 controls excitatory synaptic strength by regulating glutamatergic synapse number
- PMID: 17920015
- PMCID: PMC2198899
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuron.2007.08.018
MeCP2 controls excitatory synaptic strength by regulating glutamatergic synapse number
Abstract
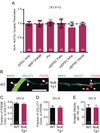
MeCP2 is a transcriptional repressor critical for normal neurological function. Prior studies demonstrated that either loss or doubling of MeCP2 results in postnatal neurodevelopmental disorders. To understand the impact of MeCP2 expression on neuronal function, we studied the synaptic properties of individual neurons from mice that either lack or express twice the normal levels of MeCP2. Hippocampal glutamatergic neurons that lack MeCP2 display a 46% reduction in synaptic response, whereas neurons with doubling of MeCP2 exhibit a 2-fold enhancement in synaptic response. Further analysis shows that these changes were primarily due to the number of synapses formed. These results reveal that MeCP2 is a key rate-limiting factor in regulating glutamatergic synapse formation in early postnatal development and that changes in excitatory synaptic strength may underlie global network alterations in neurological disorders due to altered MeCP2 levels.
Figures




References
-
- Amir RE, Van den Veyver IB, Wan M, Tran CQ, Francke U, Zoghbi HY. Rett syndrome is caused by mutations in X-linked MECP2, encoding methyl-CpG-binding protein 2. Nat Genet. 1999;23:185–188. - PubMed
-
- Armstrong D, Dunn JK, Antalffy B, Trivedi R. Selective dendritic alterations in the cortex of Rett syndrome. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1995;54:195–201. - PubMed
-
- Asaka Y, Jugloff DG, Zhang L, Eubanks JH, Fitzsimonds RM. Hippocampal synaptic plasticity is impaired in the Mecp2-null mouse model of Rett syndrome. Neurobiol Dis. 2006;21:217–227. - PubMed
-
- Belichenko PV, Hagberg B, Dahlstrom A. Morphological study of neocortical areas in Rett syndrome. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 1997;93:50–61. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

