Solid-state NMR spectroscopy of 18.5 kDa myelin basic protein reconstituted with lipid vesicles: spectroscopic characterisation and spectral assignments of solvent-exposed protein fragments
- PMID: 17920035
- PMCID: PMC3525669
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbamem.2007.08.013
Solid-state NMR spectroscopy of 18.5 kDa myelin basic protein reconstituted with lipid vesicles: spectroscopic characterisation and spectral assignments of solvent-exposed protein fragments
Abstract
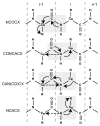
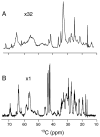
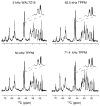
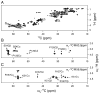
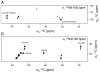
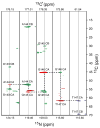
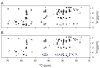
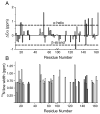
Myelin basic protein (MBP, 18.5 kDa isoform) is a peripheral membrane protein that is essential for maintaining the structural integrity of the multilamellar myelin sheath of the central nervous system. Reconstitution of the most abundant 18.5 kDa MBP isoform with lipid vesicles yields an aggregated assembly mimicking the protein's natural environment, but which is not amenable to standard solution NMR spectroscopy. On the other hand, the mobility of MBP in such a system is variable, depends on the local strength of the protein-lipid interaction, and in general is of such a time scale that the dipolar interactions are averaged out. Here, we used a combination of solution and solid-state NMR (ssNMR) approaches: J-coupling-driven polarization transfers were combined with magic angle spinning and high-power decoupling to yield high-resolution spectra of the mobile fragments of 18.5 kDa murine MBP in membrane-associated form. To partially circumvent the problem of short transverse relaxation, we implemented three-dimensional constant-time correlation experiments (NCOCX, NCACX, CONCACX, and CAN(CO)CX) that were able to provide interresidue and intraresidue backbone correlations. These experiments resulted in partial spectral assignments for mobile fragments of the protein. Additional nuclear Overhauser effect spectroscopy (NOESY)-based experiments revealed that the mobile fragments were exposed to solvent and were likely located outside the lipid bilayer, or in its hydrophilic portion. Chemical shift index analysis showed that the fragments were largely disordered under these conditions. These combined approaches are applicable to ssNMR investigations of other peripheral membrane proteins reconstituted with lipids.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Solution NMR and CD spectroscopy of an intrinsically disordered, peripheral membrane protein: evaluation of aqueous and membrane-mimetic solvent conditions for studying the conformational adaptability of the 18.5 kDa isoform of myelin basic protein (MBP).Eur Biophys J. 2008 Jul;37(6):1015-29. doi: 10.1007/s00249-008-0334-8. Epub 2008 May 1. Eur Biophys J. 2008. PMID: 18449534
-
Correlating lipid bilayer fluidity with sensitivity and resolution of polytopic membrane protein spectra by solid-state NMR spectroscopy.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015 Jan;1848(1 Pt B):334-41. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamem.2014.05.003. Epub 2014 May 13. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015. PMID: 24835018 Free PMC article.
-
Fuzzy complexes of myelin basic protein: NMR spectroscopic investigations of a polymorphic organizational linker of the central nervous system.Biochem Cell Biol. 2010 Apr;88(2):143-55. doi: 10.1139/o09-123. Biochem Cell Biol. 2010. PMID: 20453917 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Backbone resonance assignments of the 18.5 kDa isoform of murine myelin basic protein (MBP).J Biomol NMR. 2004 Aug;29(4):545-6. doi: 10.1023/B:JNMR.0000034348.99658.d7. J Biomol NMR. 2004. PMID: 15243191 No abstract available.
-
Solid-State NMR of Membrane Proteins in Lipid Bilayers: To Spin or Not To Spin?Acc Chem Res. 2021 Mar 16;54(6):1430-1439. doi: 10.1021/acs.accounts.0c00670. Epub 2021 Mar 3. Acc Chem Res. 2021. PMID: 33655754 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Proton detection for signal enhancement in solid-state NMR experiments on mobile species in membrane proteins.J Biomol NMR. 2015 Dec;63(4):375-388. doi: 10.1007/s10858-015-9997-5. Epub 2015 Oct 22. J Biomol NMR. 2015. PMID: 26494649
-
J-Based 3D sidechain correlation in solid-state proteins.Phys Chem Chem Phys. 2009 Aug 28;11(32):7078-86. doi: 10.1039/b911570f. Epub 2009 Jul 20. Phys Chem Chem Phys. 2009. PMID: 19652843 Free PMC article.
-
Myelin management by the 18.5-kDa and 21.5-kDa classic myelin basic protein isoforms.J Neurochem. 2013 May;125(3):334-61. doi: 10.1111/jnc.12195. Epub 2013 Mar 6. J Neurochem. 2013. PMID: 23398367 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Induced secondary structure and polymorphism in an intrinsically disordered structural linker of the CNS: solid-state NMR and FTIR spectroscopy of myelin basic protein bound to actin.Biophys J. 2009 Jan;96(1):180-91. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2008.10.003. Biophys J. 2009. PMID: 19134474 Free PMC article.
-
The proline-rich region of 18.5 kDa myelin basic protein binds to the SH3-domain of Fyn tyrosine kinase with the aid of an upstream segment to form a dynamic complex in vitro.Biosci Rep. 2014 Dec 8;34(6):e00157. doi: 10.1042/BSR20140149. Biosci Rep. 2014. PMID: 25343306 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Harauz G, Ishiyama N, Hill CMD, Bates IR, Libich DS, Farès C. Myelin basic protein—diverse conformational states of an intrinsically unstructured protein and its roles in myelin assembly and multiple sclerosis. Micron. 2004;35:503–542. - PubMed
-
- Bates IR, Boggs JM, Feix JB, Harauz G. Membrane-anchoring and charge effects in the interaction of myelin basic protein with lipid bilayers studied by site-directed spin labeling. J Biol Chem. 2003;278:29041–29047. - PubMed
-
- Bates IR, Feix JB, Boggs JM, Harauz G. An immunodominant epitope of myelin basic protein is an amphipathic alpha-helix. J Biol Chem. 2004;279:5757–5764. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

