The effects of normal aging and ApoE genotype on the levels of CSF biomarkers for Alzheimer's disease
- PMID: 17920160
- PMCID: PMC2774788
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2007.08.019
The effects of normal aging and ApoE genotype on the levels of CSF biomarkers for Alzheimer's disease
Abstract
While cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) biomarkers are of use in the prediction and diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease our understanding of the background effects of age and the ApoE genotype is limited. Seventy-eight community-based normal volunteers (mean age 60+/-10 years, range 36-86) were examined to determine the relationships between CSF measures of total tau (T-tau), hyperphosphorylated tau (P-tau 231), amyloid beta (Abeta42/Abeta40 ratio), and isoprostane (IP) with age and ApoE genotype. The results showed that age by epsilon4 genotype interactions were found for P-tau231 (beta=1.82; p<0.05) and IP (beta=1.6; p<0.05). T-tau CSF concentration increased with age. The increasing CSF concentrations of P-tau and IP in epsilon4 carriers suggest that early tauopathy and oxidative stress may be related to the increased risk for AD. The data also suggest that T-tau changes are more age dependent than Abeta changes. The evidence that P-tau231 and IP are the earliest markers for the neuronal damage related to AD awaits longitudinal study.
Figures
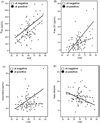
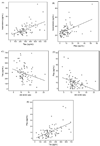
References
-
- Arai H, Morikawa Y, Higuchi M, Matsui T, Clark CM, Miura M, Machida N, Lee VM, Trojanowski JQ, Sasaki H. Cere-brospinal fluid tau levels in neurodegenerative diseases with distinct tau-related pathology. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1997;236:262–264. - PubMed
-
- Augustinack JC, Schneider A, Mandelkow EM, Hyman BT. Specific tau phosphorylation sites correlate with severity of neuronal cytopathology in Alzheimer’s disease. Acta Neuropatholog. 2002;103(1):26–35. - PubMed
-
- Bachman DL, Wolf MD, Linn R, Knoefel JE, Cobb J, Belanger BS, D’Agostino RB, White LR. Incidence of dementia and probable Alzheimer’s disease in a general population: the Framingham Study. Neurology. 1993;43:515–519. - PubMed
-
- Bennett DA, Schneider JA, Arvanitakis Z, Kelly JF, Aggarwal NT, Shah RC, Wilson RS. Neuropathology of older persons without cognitive impairment from two community-based studies. Neurology. 2006;66(12):1837–1844. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

