Alpha 1-noradrenergic system role in increased motivation for cocaine intake in rats with prolonged access
- PMID: 17920248
- PMCID: PMC2376122
- DOI: 10.1016/j.euroneuro.2007.08.003
Alpha 1-noradrenergic system role in increased motivation for cocaine intake in rats with prolonged access
Abstract
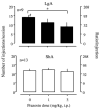
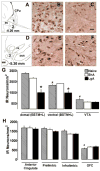
In rodents, extended access to cocaine produces an escalation in cocaine self-administration that has face and construct validity for human compulsive drug intake. Here we report that rats with six-hour access (long access, LgA) to cocaine self-administration produced a higher breakpoint for cocaine using a progressive-ratio schedule than rats with one-hour access (short access, ShA), and prazosin (alpha 1 receptor antagonist) reduced the higher breakpoint for cocaine in LgA rats. Additionally, the number of neurons with alpha 1-adrenergic receptor-like immunoreactivity in the bed nucleus of stria terminalis (BNST) was found to be much lower in LgA rats than in ShA and drug-naive rats. In contrast, UK14304 (alpha 2 receptor agonist) and betaxolol (beta 1 receptor antagonist) had no effect on cocaine self-administration in either group. The data suggest that activation of the alpha 1-noradrenergic system, perhaps in the BNST, is associated with increased motivation for cocaine in rats with extended access.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest
All the authors (S.W., C.D.M., D.M.L., G.F.K.) have no conflict of interest to declare.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Previous exposure to cocaine enhances cocaine self-administration in an alpha 1-adrenergic receptor dependent manner.Neuropsychopharmacology. 2007 Mar;32(3):638-45. doi: 10.1038/sj.npp.1301120. Epub 2006 Jun 14. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2007. PMID: 16794571
-
Inhibition of kappa opioid receptors attenuated increased cocaine intake in rats with extended access to cocaine.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2009 Sep;205(4):565-75. doi: 10.1007/s00213-009-1563-y. Epub 2009 May 30. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2009. PMID: 19484223 Free PMC article.
-
Blockade of stress-induced but not cocaine-induced reinstatement by infusion of noradrenergic antagonists into the bed nucleus of the stria terminalis or the central nucleus of the amygdala.J Neurosci. 2002 Jul 1;22(13):5713-8. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.22-13-05713.2002. J Neurosci. 2002. PMID: 12097523 Free PMC article.
-
α(2) Adrenergic and imidazoline receptor agonists prevent cue-induced cocaine seeking.Biol Psychiatry. 2011 Oct 15;70(8):712-719. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2011.06.010. Epub 2011 Jul 23. Biol Psychiatry. 2011. PMID: 21783176 Free PMC article.
-
How to make a rat addicted to cocaine.Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2007 Nov 15;31(8):1614-24. doi: 10.1016/j.pnpbp.2007.08.028. Epub 2007 Aug 28. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2007. PMID: 17888555 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Neurobiological mechanisms that contribute to stress-related cocaine use.Neuropharmacology. 2014 Jan;76 Pt B(0 0):383-94. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2013.07.021. Epub 2013 Aug 2. Neuropharmacology. 2014. PMID: 23916481 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The speed of cocaine delivery determines the subsequent motivation to self-administer the drug.Neuropsychopharmacology. 2013 Dec;38(13):2644-56. doi: 10.1038/npp.2013.173. Epub 2013 Jul 18. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2013. PMID: 23921953 Free PMC article.
-
Chronic administration of a norepinephrine antagonist prevents and partially reverses escalation of cocaine self-administration.Addict Biol. 2023 Sep;28(9):e13316. doi: 10.1111/adb.13316. Addict Biol. 2023. PMID: 37644893 Free PMC article.
-
Neuroclinical Framework for the Role of Stress in Addiction.Chronic Stress (Thousand Oaks). 2017 Feb;1:2470547017698140. doi: 10.1177/2470547017698140. Epub 2017 Apr 10. Chronic Stress (Thousand Oaks). 2017. PMID: 28653044 Free PMC article.
-
The selective dopamine β-hydroxylase inhibitor nepicastat attenuates multiple aspects of cocaine-seeking behavior.Neuropsychopharmacology. 2013 May;38(6):1032-8. doi: 10.1038/npp.2012.267. Epub 2013 Jan 3. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2013. PMID: 23303068 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ahmed SH, Koob GF. Transition from moderate to excessive drug intake: change in hedonic set point. Science. 1998;282:298–300. - PubMed
-
- Ahmed SH, Koob GF. Long-lasting increase in the set point for cocaine self-administration after escalation in rats. Psychopharmacology. 1999;146:303–312. - PubMed
-
- Andorn AC, Carlson MA, Gilkeson RC. Specific [3H]UK 14,304 binding in human cortex occurs at multiple high affinity states with alpha 2-adrenergic selectivity and differing affinities for GTP. Life Sci. 1988;43:1805–1812. - PubMed
-
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, IV-TR. American Psychiatry Press; Washington, D: 2000.
-
- Aston-Jones G, Delfs JM, Druhan J, Zhu Y. The bed nucleus of the stria terminalis. A target site for noradrenergic actions in opiate withdrawal. Ann NY Acad Sci. 1999;877:486–498. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

