Quantitative PCR technique for detecting lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus in vivo
- PMID: 17920702
- PMCID: PMC2330273
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jviromet.2007.08.025
Quantitative PCR technique for detecting lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus in vivo
Abstract
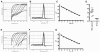
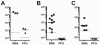
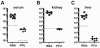
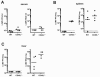
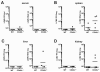
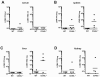
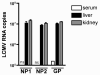
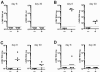
Quantitative PCR (QPCR, or real time PCR (rtPCR)) has emerged as a powerful virologic technique for measuring viral replication and viral loads in humans and animal models. We have developed a QPCR assay to accurately quantify lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus (LCMV) in infected mice. We first validated this assay using plasmid DNA and LCMV viral stocks. We then demonstrated that the LCMV QPCR assay can detect LCMV in serum and tissues of chronically infected mice (LCMV-clone 13), with greater sensitivity than conventional plaque assay. Subsequently, we demonstrated that the QPCR assay can detect LCMV in tissues of CD40L(-/-) mice during a low grade chronic infection with LCMV Armstrong. Finally, we improved the assay further such that it was approximate 1000-fold more sensitive than plaque assay for detection of the presence of LCMV in tissue.
Figures

References
-
- Bachmann MF, Hunziker L, Zinkernagel RM, Storni T, Kopf M. Maintenance of memory CTL responses by T helper cells and CD40-CD40 ligand: antibodies provide the key. Eur J Immunol. 2004;34:317–26. - PubMed
-
- Buchmeier MJ, Zajac A. Lymphocytic Choriomeningitis Virus. In: Ahmed R, Chen I, editors. Persistent Viral Infections. John Wiley and Sons; 1999. pp. 575–605.
-
- Crotty S, Kersh EN, Cannons J, Schwartzberg PL, Ahmed R. SAP is required for generating long-term humoral immunity. Nature. 2003;421:282–7. - PubMed
-
- Crotty S, McCausland MM, Aubert RD, Wherry EJ, Ahmed R. Hypogammaglobulinemia and exacerbated CD8 T-cell-mediated immunopathology in SAP-deficient mice with chronic LCMV infection mimics human XLP disease. Blood. 2006;108:3085–93. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

