The high affinity peripheral benzodiazepine receptor ligand DAA1106 binds to activated and infected brain macrophages in areas of synaptic degeneration: implications for PET imaging of neuroinflammation in lentiviral encephalitis
- PMID: 17920902
- PMCID: PMC2258458
- DOI: 10.1016/j.nbd.2007.08.016
The high affinity peripheral benzodiazepine receptor ligand DAA1106 binds to activated and infected brain macrophages in areas of synaptic degeneration: implications for PET imaging of neuroinflammation in lentiviral encephalitis
Abstract
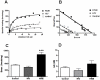
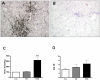
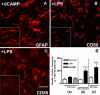
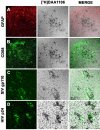
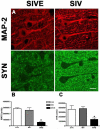
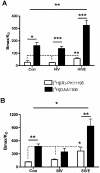
HIV encephalitis (HIVE) is characterized by neurodegeneration mediated by toxins derived from infected and activated brain macrophages. Since the peripheral benzodiazepine receptor (PBR) is abundant on brain macrophages, we hypothesized that [(3)H]DAA1106, a new PBR ligand, can label infected and activated brain macrophages in HIVE. Using cell culture and postmortem brain tissues from HIVE and a macaque model of HIVE, we show that [(3)H]DAA1106 binds with high affinity to activated and infected macrophages in regions of synaptic damage. Further, binding affinity reflected by lower K(D) (dissociation constant) values and the B(max) (total number of binding sites) to K(D) ratios reflective of ligand-binding potential was significantly higher with [(3)H]DAA1106 compared to the extensively characterized PBR ligand [(3)H](R)-PK11195. These data suggest that DAA1106 binds with high affinity to activated and infected brain macrophages and possesses binding characteristics beneficial for in vivo use in the detection and clinical monitoring of HIVE using positron emission tomography.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The positron emission tomography ligand DAA1106 binds with high affinity to activated microglia in human neurological disorders.J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 2008 Oct;67(10):1001-10. doi: 10.1097/NEN.0b013e318188b204. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 2008. PMID: 18800007 Free PMC article.
-
Longitudinal in vivo positron emission tomography imaging of infected and activated brain macrophages in a macaque model of human immunodeficiency virus encephalitis correlates with central and peripheral markers of encephalitis and areas of synaptic degeneration.Am J Pathol. 2008 Jun;172(6):1603-16. doi: 10.2353/ajpath.2008.070967. Epub 2008 May 8. Am J Pathol. 2008. PMID: 18467697 Free PMC article.
-
A comparison of the high-affinity peripheral benzodiazepine receptor ligands DAA1106 and (R)-PK11195 in rat models of neuroinflammation: implications for PET imaging of microglial activation.J Neurochem. 2007 Sep;102(6):2118-2131. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2007.04690.x. Epub 2007 Jun 7. J Neurochem. 2007. PMID: 17555551
-
[Imaging of glial cells by positron-emitted peripheral benzodiazepine receptor ligands].Nihon Shinkei Seishin Yakurigaku Zasshi. 2006 Feb;26(1):17-21. Nihon Shinkei Seishin Yakurigaku Zasshi. 2006. PMID: 16637592 Review. Japanese.
-
N-Acetyl-N-(2-[18F]fluoroethoxybenzyl)-2-phenoxy-5-pyridinamine.2008 Aug 12 [updated 2008 Aug 22]. In: Molecular Imaging and Contrast Agent Database (MICAD) [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Center for Biotechnology Information (US); 2004–2013. 2008 Aug 12 [updated 2008 Aug 22]. In: Molecular Imaging and Contrast Agent Database (MICAD) [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Center for Biotechnology Information (US); 2004–2013. PMID: 20641889 Free Books & Documents. Review.
Cited by
-
Cyclooxygenase and neuroinflammation in Parkinson's disease neurodegeneration.Curr Neuropharmacol. 2010 Mar;8(1):62-8. doi: 10.2174/157015910790909485. Curr Neuropharmacol. 2010. PMID: 20808546 Free PMC article.
-
The positron emission tomography ligand DAA1106 binds with high affinity to activated microglia in human neurological disorders.J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 2008 Oct;67(10):1001-10. doi: 10.1097/NEN.0b013e318188b204. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 2008. PMID: 18800007 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of the translocator protein of 18 kDa by microglia, macrophages and astrocytes based on immunohistochemical localization in abnormal human brain.Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol. 2009 Jun;35(3):306-28. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2990.2008.01006.x. Epub 2008 Dec 11. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol. 2009. PMID: 19077109 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of translocator protein quantification as a tool for characterising macrophage burden in human carotid atherosclerosis.Atherosclerosis. 2010 Jun;210(2):388-91. doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2009.11.047. Epub 2009 Dec 4. Atherosclerosis. 2010. PMID: 20056222 Free PMC article.
-
18 kDa TSPO targeting drives polarized human microglia towards a protective and restorative neurosteroidome profile.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2025 Jan 6;82(1):34. doi: 10.1007/s00018-024-05544-1. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2025. PMID: 39757281 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abe K, Saito H. The p44/42 mitogen-activated protein kinase cascade is involved in the induction and maintenance of astrocyte stellation mediated by protein kinase C. Neurosci Res. 2000;36:251–257. - PubMed
-
- Banati RB. Visualising microglial activation in vivo. Glia. 2002;40:206–217. - PubMed
-
- Banati RB, Newcombe J, Gunn RN, Cagnin A, Turkheimer F, Heppner F, Price G, Wegner F, Giovannoni G, Miller DH, Perkin GD, Smith T, Hewson AK, Bydder G, Kreutzberg GW, Jones T, Cuzner ML, Myers R. The peripheral benzodiazepine binding site in the brain in multiple sclerosis: quantitative in vivo imaging of microglia as a measure of disease activity. Brain. 2000;123(Pt 11):2321–2337. - PubMed
-
- Barami K, Grever WE, Diaz FG, Lyman WD. An efficient method for the culturing and generation of neurons and astrocytes from second trimester human central nervous system tissue. Neurol Res. 2001;23:321–326. - PubMed
-
- Bergamini A, Faggioli E, Bolacchi F, Gessani S, Cappannoli L, Uccella I, Demin F, Capozzi M, Cicconi R, Placido R, Vendetti S, Colizzi GM, Rocchi G. Enhanced production of tumor necrosis factor-alpha and interleukin-6 due to prolonged response to lipopolysaccharide in human macrophages infected in vitro with human immunodeficiency virus type 1. J Infect Dis. 1999;179:832–842. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

