Quantitative distributions of Epsilonproteobacteria and a Sulfurimonas subgroup in pelagic redoxclines of the central Baltic Sea
- PMID: 17921285
- PMCID: PMC2168200
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.00466-07
Quantitative distributions of Epsilonproteobacteria and a Sulfurimonas subgroup in pelagic redoxclines of the central Baltic Sea
Abstract
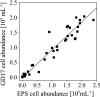
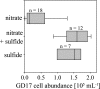
Members of the class Epsilonproteobacteria are known to be of major importance in biogeochemical processes at oxic-anoxic interfaces. In pelagic redoxclines of the central Baltic Sea, an uncultured epsilonproteobacterium related to Sulfurimonas denitrificans was proposed to play a key role in chemolithotrophic denitrification (I. Brettar, M. Labrenz, S. Flavier, J. Bötel, H. Kuosa, R. Christen, and M. G. Höfle, Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 72:1364-1372, 2006). In order to determine the abundance, activity, and vertical distribution of this bacterium in high-resolution profiles, 16S rRNA cloning and catalyzed reporter deposition and fluorescence in situ hybridization (CARD-FISH) and quantitative PCR measurements were carried out. The results showed that 21% of the derived clone sequences, which in the present study were grouped together under the name GD17, had >99% similarity to the uncultured epsilonproteobacterium. A specific gene probe against GD17 (S-*-Sul-0090-a-A-18) was developed and used for enumeration by CARD-FISH. In different pelagic redoxclines sampled during August 2003, May 2005, and February 2006, GD17 cells were always detected from the lower oxic area to the sulfidic area. Maximal abundance was detected around the chemocline, where sulfide and nitrate concentrations were close to the detection limit. The highest GD17 numbers (2 x 10(5) cells ml(-1)), representing up to 15% of the total bacteria, were comparable to those reported for Epsilonproteobacteria in pelagic redoxclines of the Black Sea and the Cariaco Trench (X. Lin, S. G. Wakeham, I. F. Putnam, Y. M. Astor, M. I. Scranton, A. Y. Chistoserdov, and G. T. Taylor, Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 72:2679-2690, 2006). However, in the Baltic Sea redoxclines, Epsilonproteobacteria consisted nearly entirely of cells belonging to the distinct GD17 group. This suggested that GD17 was the best-adapted epsilonproteobacterium within this ecological niche.
Figures




References
-
- Altschul, S. F., W. Gish, W. Miller, E. W. Myers, and D. J. Lipman. 1990. Basic local alignment search tool. J. Mol. Biol. 215:403-410. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

