Rhodobacter capsulatus OlsA is a bifunctional enzyme active in both ornithine lipid and phosphatidic acid biosynthesis
- PMID: 17921310
- PMCID: PMC2168953
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.01121-07
Rhodobacter capsulatus OlsA is a bifunctional enzyme active in both ornithine lipid and phosphatidic acid biosynthesis
Abstract
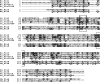
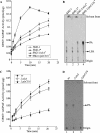
The Rhodobacter capsulatus genome contains three genes (olsA [plsC138], plsC316, and plsC3498) that are annotated as lysophosphatidic acid (1-acyl-sn-glycerol-3-phosphate) acyltransferase (AGPAT). Of these genes, olsA was previously shown to be an O-acyltransferase in the second step of ornithine lipid biosynthesis, which is important for optimal steady-state levels of c-type cytochromes (S. Aygun-Sunar, S. Mandaci, H.-G. Koch, I. V. J. Murray, H. Goldfine, and F. Daldal. Mol. Microbiol. 61:418-435, 2006). The roles of the remaining plsC316 and plsC3498 genes remained unknown. In this work, these genes were cloned, and chromosomal insertion-deletion mutations inactivating them were obtained to define their function. Characterization of these mutants indicated that, unlike the Escherichia coli plsC, neither plsC316 nor plsC3498 was essential in R. capsulatus. In contrast, no plsC316 olsA double mutant could be isolated, indicating that an intact copy of either olsA or plsC316 was required for R. capsulatus growth under the conditions tested. Compared to OlsA null mutants, PlsC316 null mutants contained ornithine lipid and had no c-type cytochrome-related phenotype. However, they exhibited slight growth impairment and highly altered total fatty acid and phospholipid profiles. Heterologous expression in an E. coli plsC(Ts) mutant of either R. capsulatus plsC316 or olsA gene products supported growth at a nonpermissive temperature, exhibited AGPAT activity in vitro, and restored phosphatidic acid biosynthesis. The more vigorous AGPAT activity displayed by PlsC316 suggested that plsC316 encodes the main AGPAT required for glycerophospholipid synthesis in R. capsulatus, while olsA acts as an alternative AGPAT that is specific for ornithine lipid synthesis. This study therefore revealed for the first time that some OlsA enzymes, like the enzyme of R. capsulatus, are bifunctional and involved in both membrane ornithine lipid and glycerophospholipid biosynthesis.
Figures

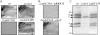

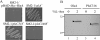
Similar articles
-
Thematic review series: Glycerolipids. Acyltransferases in bacterial glycerophospholipid synthesis.J Lipid Res. 2008 Sep;49(9):1867-74. doi: 10.1194/jlr.R800005-JLR200. Epub 2008 Mar 27. J Lipid Res. 2008. PMID: 18369234 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification of a 1-acyl-glycerol-3-phosphate acyltransferase from Mycobacterium tuberculosis, a key enzyme involved in triacylglycerol biosynthesis.Mol Microbiol. 2024 Jun;121(6):1164-1181. doi: 10.1111/mmi.15265. Epub 2024 Apr 26. Mol Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 38676355
-
Identification of a gene required for the formation of lyso-ornithine lipid, an intermediate in the biosynthesis of ornithine-containing lipids.Mol Microbiol. 2004 Sep;53(6):1757-70. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2004.04240.x. Mol Microbiol. 2004. PMID: 15341653
-
The dithiol:disulfide oxidoreductases DsbA and DsbB of Rhodobacter capsulatus are not directly involved in cytochrome c biogenesis, but their inactivation restores the cytochrome c biogenesis defect of CcdA-null mutants.J Bacteriol. 2003 Jun;185(11):3361-72. doi: 10.1128/JB.185.11.3361-3372.2003. J Bacteriol. 2003. PMID: 12754234 Free PMC article.
-
Phosphatidic acid biosynthesis in the model organism yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae - a survey.Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Biol Lipids. 2021 Jun;1866(6):158907. doi: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2021.158907. Epub 2021 Feb 18. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Biol Lipids. 2021. PMID: 33610760 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Alternative lipid synthesis in response to phosphate limitation promotes antibiotic tolerance in Gram-negative ESKAPE pathogens.PLoS Pathog. 2025 Feb 7;21(2):e1012933. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1012933. eCollection 2025 Feb. PLoS Pathog. 2025. PMID: 39919117 Free PMC article.
-
Biogenesis of cbb(3)-type cytochrome c oxidase in Rhodobacter capsulatus.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2012 Jun;1817(6):898-910. doi: 10.1016/j.bbabio.2011.10.011. Epub 2011 Nov 4. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2012. PMID: 22079199 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Alternative lipid synthesis in response to phosphate limitation promotes antibiotic tolerance in Gram-negative ESKAPE pathogens.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Dec 31:2024.09.11.612458. doi: 10.1101/2024.09.11.612458. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: PLoS Pathog. 2025 Feb 07;21(2):e1012933. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1012933. PMID: 39314339 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Production of long-chain free fatty acids from metabolically engineered Rhodobacter sphaeroides heterologously producing periplasmic phospholipase A2 in dodecane-overlaid two-phase culture.Microb Cell Fact. 2019 Jan 31;18(1):20. doi: 10.1186/s12934-019-1070-8. Microb Cell Fact. 2019. PMID: 30704481 Free PMC article.
-
Thematic review series: Glycerolipids. Acyltransferases in bacterial glycerophospholipid synthesis.J Lipid Res. 2008 Sep;49(9):1867-74. doi: 10.1194/jlr.R800005-JLR200. Epub 2008 Mar 27. J Lipid Res. 2008. PMID: 18369234 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Aguado, B., and R. D. Campbell. 1998. Characterization of a human lysophosphatidic acid acyltransferase that is encoded by a gene located in the class III region of the human major histocompatibility complex. J. Biol. Chem. 273:4096-4105. - PubMed
-
- Athenstaedt, K., and G. Daum. 1999. Phosphatidic acid, a key intermediate in lipid metabolism. Eur. J. Biochem. 266:1-16. - PubMed
-
- Aygun-Sunar, S., S. Mandaci, H.-G. Koch, I. V. J. Murray, H. Goldfine, and F. Daldal. 2006. Ornithine lipid is required for optimal steady-state amounts of c-type cytochromes in Rhodobacter capsulatus. Mol. Microbiol. 61:418-435. - PubMed
-
- Baysse, C., M. Cullinane, V. Denervaud, E. Burrowes, J. M. Dow, J. P. Morrissey, L. Tam, J. T. Trevors, and F. O'Gara. 2005. Modulation of quorum sensing in Pseudomonas aeruginosa through alteration of membrane properties. Microbiology 151:2529-2542. - PubMed
-
- Bonham, L., D. W. Leung, T. White, D. Hollenback, P. Klein, J. Tulinsky, M. Coon, P. De Vries, and J. W. Singer. 2003. Lysophosphatidic acid acyltransferase-beta: a novel target for induction of tumour cell apoptosis. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 7:643-661. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

