Differential requirements for RAD51 in Physcomitrella patens and Arabidopsis thaliana development and DNA damage repair
- PMID: 17921313
- PMCID: PMC2174717
- DOI: 10.1105/tpc.107.054049
Differential requirements for RAD51 in Physcomitrella patens and Arabidopsis thaliana development and DNA damage repair
Abstract
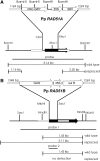
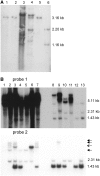
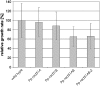
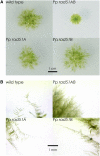
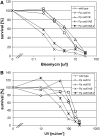
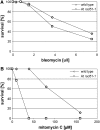
RAD51, the eukaryotic homolog of the bacterial RecA recombinase, plays a central role in homologous recombination (HR) in yeast and animals. Loss of RAD51 function causes lethality in vertebrates but not in other animals or in the flowering plant Arabidopsis thaliana, suggesting that RAD51 is vital for highly developed organisms but not for others. Here, we found that loss of RAD51 function in the moss Physcomitrella patens, a plant of less complexity, caused a significant vegetative phenotype, indicating an important function for RAD51 in this organism. Moreover, loss of RAD51 caused marked hypersensitivity to the double-strand break-inducing agent bleomycin in P. patens but not in Arabidopsis. Therefore, HR is used for somatic DNA damage repair in P. patens but not in Arabidopsis. These data imply fundamental differences in the use of recombination pathways between plants. Moreover, these data demonstrate that the importance of RAD51 for viability is independent of taxonomic position or complexity of an organism. The involvement of HR in DNA damage repair in the slowly evolving species P. patens but not in fast-evolving Arabidopsis suggests that the choice of the recombination pathway is related to the speed of evolution in plants.
Figures
Similar articles
-
RAD51 loss of function abolishes gene targeting and de-represses illegitimate integration in the moss Physcomitrella patens.DNA Repair (Amst). 2010 May 4;9(5):526-33. doi: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2010.02.001. Epub 2010 Mar 1. DNA Repair (Amst). 2010. PMID: 20189889
-
RAD51B plays an essential role during somatic and meiotic recombination in Physcomitrella.Nucleic Acids Res. 2014 Oct 29;42(19):11965-78. doi: 10.1093/nar/gku890. Epub 2014 Sep 26. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014. PMID: 25260587 Free PMC article.
-
CRISPR-Cas9-mediated efficient directed mutagenesis and RAD51-dependent and RAD51-independent gene targeting in the moss Physcomitrella patens.Plant Biotechnol J. 2017 Jan;15(1):122-131. doi: 10.1111/pbi.12596. Epub 2016 Jul 22. Plant Biotechnol J. 2017. PMID: 27368642 Free PMC article.
-
The rDNA Loci-Intersections of Replication, Transcription, and Repair Pathways.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jan 28;22(3):1302. doi: 10.3390/ijms22031302. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33525595 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Function and molecular mechanisms of APE2 in genome and epigenome integrity.Mutat Res Rev Mutat Res. 2021 Jan-Jun;787:108347. doi: 10.1016/j.mrrev.2020.108347. Epub 2020 Nov 16. Mutat Res Rev Mutat Res. 2021. PMID: 34083046 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Reannotation and extended community resources for the genome of the non-seed plant Physcomitrella patens provide insights into the evolution of plant gene structures and functions.BMC Genomics. 2013 Jul 23;14:498. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-14-498. BMC Genomics. 2013. PMID: 23879659 Free PMC article.
-
Gene Targeting Without DSB Induction Is Inefficient in Barley.Front Plant Sci. 2017 Jan 5;7:1973. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2016.01973. eCollection 2016. Front Plant Sci. 2017. PMID: 28105032 Free PMC article.
-
The Importance of ATM and ATR in Physcomitrella patens DNA Damage Repair, Development, and Gene Targeting.Genes (Basel). 2020 Jul 6;11(7):752. doi: 10.3390/genes11070752. Genes (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32640722 Free PMC article.
-
Inroads into saline-alkaline stress response in plants: unravelling morphological, physiological, biochemical, and molecular mechanisms.Planta. 2024 Apr 22;259(6):130. doi: 10.1007/s00425-024-04368-4. Planta. 2024. PMID: 38647733 Review.
-
Homologous pairing activities of two rice RAD51 proteins, RAD51A1 and RAD51A2.PLoS One. 2013 Oct 4;8(10):e75451. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0075451. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24124491 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alpi, A., Pasierbek, P., Gartner, A., and Loidl, J. (2003). Genetic and cytological characterization of the recombination protein RAD51 in Caenorhabditis elegans. Chromosoma 112 6–16. - PubMed
-
- Ashton, N.W., and Cove, D.J. (1977). The isolation and preliminary characterization of auxotrophic and analog resistant mutants of the moss Physcomitrella patens. Mol. Gen. Genet. 154 87–96.
-
- Ayora, S., Piruat, J.I., Luna, R., Reiss, B., Russo, V.E.A., Aguilera, A., and Alonso, J.C. (2002). Characterization of two highly similar Rad51 homologs of Physcomitrella patens. J. Mol. Biol. 316 35–49. - PubMed
-
- Baumann, P., and West, S.C. (1998). Role of the human RAD51 protein in homologous recombination and double-stranded-break repair. Trends Biochem. Sci. 23 247–251. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

