Arabidopsis cotyledon-specific chloroplast biogenesis factor CYO1 is a protein disulfide isomerase
- PMID: 17921316
- PMCID: PMC2174705
- DOI: 10.1105/tpc.107.051714
Arabidopsis cotyledon-specific chloroplast biogenesis factor CYO1 is a protein disulfide isomerase
Abstract
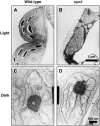
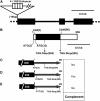
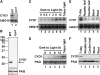
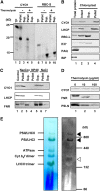
Chloroplast development in cotyledons differs in a number of ways from that in true leaves, but the cotyledon-specific program of chloroplast biogenesis has not been clarified. The cyo1 mutant in Arabidopsis thaliana has albino cotyledons but normal green true leaves. Chloroplasts develop abnormally in cyo1 mutant plants grown in the light, but etioplasts are normal in mutants grown in the dark. We isolated CYO1 by T-DNA tagging and verified that the mutant allele was responsible for the albino cotyledon phenotype by complementation. CYO1 has a C(4)-type zinc finger domain similar to that of Escherichia coli DnaJ. CYO1 is expressed mainly in young plants under light conditions, and the CYO1 protein localizes to the thylakoid membrane in chloroplasts. Transcription of nuclear photosynthetic genes is generally unaffected by the cyo1 mutation, but the level of photosynthetic proteins is decreased in cyo1 mutants. Recombinant CYO1 accelerates disulfide bond reduction in the model substrate insulin and renatures RNase A, indicating that CYO1 has protein disulfide isomerase activity. These results suggest that CYO1 has a chaperone-like activity required for thylakoid biogenesis in cotyledons.
Figures


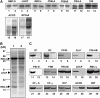
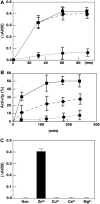
References
-
- Albrecht, V., Ingenfeld, A., and Apel, K. (2006). Characterization of the snowy cotyledon 1 mutant of Arabidopsis thaliana: The impact of chloroplast elongation factor G on chloroplast development and plant vitality. Plant Mol. Biol. 60 507–518. - PubMed
-
- Anfinsen, C.B., and Scheraga, H.A. (1975). Experimental and theoretical aspects of protein folding. Adv. Protein Chem. 29 205–300. - PubMed
-
- Aronsson, H., and Jarvis, P. (2002). A simple method for isolating import-competent Arabidopsis chloroplasts. FEBS Lett. 529 215–220. - PubMed
-
- Awai, K., Marechal, E., Block, M.A., Brun, D., Masuda, T., Shimada, H., Takamiya, K., Ohta, H., and Joyard, J. (2001). Two types of MGDG synthase genes, found widely in both 16:3 and 18:3 plants, differentially mediate galactolipid syntheses in photosynthetic and nonphotosynthetic tissues in Arabidopsis thaliana. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 98 10960–10965. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

