PTEN: a promising pharmacological target to enhance epithelial wound healing
- PMID: 17922021
- PMCID: PMC2189987
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0707503
PTEN: a promising pharmacological target to enhance epithelial wound healing
Abstract
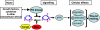
PI3Ks (phosphoinositide-3 kinases) produce PIP3 (phosphatidylinositol(3,4,5)-trisphosphate) which mediates signals for cell survival and proliferation. The tumour suppressor PTEN (phosphatase and tensin homologue) dephosphorylates PIP3 and is a key negative regulator of PI3K signalling. Recent research highlighted important roles for PI3K/PTEN in cell polarization and directional cell migration, pointing to a significant role for PTEN in wound healing where spatially organized tissue growth is essential. Lai et al. (in this issue of British Journal of Pharmacology) have moved a step closer in utilizing PTEN for wound healing through pharmacological inhibition. Two vanadium derivative inhibitors targeting PTEN significantly elevated the level of phosphorylated Akt (protein kinase B) and nearly doubled the wound healing rate in monolayer cultures of lung and airway epithelial cells. Damage to airway and lung epithelia underlies a wide spectrum of significant clinical conditions. With further experiments, this promising approach may find potential clinical use in situations where enhanced wound healing of pulmonary and other epithelia is important.
Figures
Comment on
-
Phosphatase and tensin homologue deleted on chromosome ten (PTEN) as a molecular target in lung epithelial wound repair.Br J Pharmacol. 2007 Dec;152(8):1172-84. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0707501. Epub 2007 Oct 8. Br J Pharmacol. 2007. PMID: 17922022 Free PMC article.
Similar articles
-
Phosphatase and tensin homologue deleted on chromosome ten (PTEN) as a molecular target in lung epithelial wound repair.Br J Pharmacol. 2007 Dec;152(8):1172-84. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0707501. Epub 2007 Oct 8. Br J Pharmacol. 2007. PMID: 17922022 Free PMC article.
-
PTEN inhibition improves wound healing in lung epithelia through changes in cellular mechanics that enhance migration.Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2012 Feb 1;302(3):L287-99. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00037.2011. Epub 2011 Oct 28. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2012. PMID: 22037358 Free PMC article.
-
Downregulation of PTEN at corneal wound sites accelerates wound healing through increased cell migration.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2011 Apr 8;52(5):2272-8. doi: 10.1167/iovs.10-5972. Print 2011 Apr. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2011. PMID: 21212174 Free PMC article.
-
PTEN Inhibition in Human Disease Therapy.Molecules. 2018 Jan 30;23(2):285. doi: 10.3390/molecules23020285. Molecules. 2018. PMID: 29385737 Free PMC article. Review.
-
PTEN/PTENP1: 'Regulating the regulator of RTK-dependent PI3K/Akt signalling', new targets for cancer therapy.Mol Cancer. 2018 Feb 19;17(1):37. doi: 10.1186/s12943-018-0803-3. Mol Cancer. 2018. PMID: 29455665 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Cytokeratin profile and keratinocyte gene expression in keratinized lid margins of patients with chronic Stevens-Johnson syndrome.Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2022 Sep;260(9):3009-3018. doi: 10.1007/s00417-022-05669-8. Epub 2022 Apr 23. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2022. PMID: 35460363
-
The biomolecular basis of adipogenic differentiation of adipose-derived stem cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2014 Apr 16;15(4):6517-26. doi: 10.3390/ijms15046517. Int J Mol Sci. 2014. PMID: 24743893 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Akt inhibition up-regulates MMP1 through a CCN2-dependent pathway in human dermal fibroblasts.Exp Dermatol. 2010 Apr;19(4):347-54. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0625.2010.01065.x. Epub 2010 Feb 25. Exp Dermatol. 2010. PMID: 20201953 Free PMC article.
-
Harnessing the Electric Spark of Life to Cure Skin Wounds.Adv Wound Care (New Rochelle). 2014 Feb 1;3(2):127-138. doi: 10.1089/wound.2013.0451. Adv Wound Care (New Rochelle). 2014. PMID: 24761353 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Function and dysfunction of the PI system in membrane trafficking.EMBO J. 2008 Oct 8;27(19):2457-70. doi: 10.1038/emboj.2008.169. Epub 2008 Sep 11. EMBO J. 2008. PMID: 18784754 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Block ER, Matela AR, SundarRaj N, Iszkula ER, Klarlund JK. Wounding induces motility in sheets of corneal epithelial cells through loss of spatial constraints: role of heparin-binding epidermal growth factor-like growth factor signaling. J Biol Chem. 2004;279:24307–24312. - PubMed
-
- Comer FI, Parent CA. Phosphoinositides specify polarity during epithelial organ development. Cell. 2007;128:239–240. - PubMed
-
- Cully M, You H, Levine AJ, Mak TW. Beyond PTEN mutations: the PI3K pathway as an integrator of multiple inputs during tumorigenesis. Nat Rev Cancer. 2006;6:184–192. - PubMed
-
- Engelman JA, Luo J, Cantley LC. The evolution of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinases as regulators of growth and metabolism. Nat Rev Genet. 2006;7:606–619. - PubMed
-
- Huttenlocher A, Horwitz AR. Wound healing with electric potential. N Engl J Med. 2007;356:303–304. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

