The presence of carboxypeptidase-M in tumour cells signifies epidermal growth factor receptor expression in lung adenocarcinomas: the coexistence predicts a poor prognosis regardless of EGFR levels
- PMID: 17922141
- PMCID: PMC12161634
- DOI: 10.1007/s00432-007-0304-z
The presence of carboxypeptidase-M in tumour cells signifies epidermal growth factor receptor expression in lung adenocarcinomas: the coexistence predicts a poor prognosis regardless of EGFR levels
Abstract
Purpose: Carboxypeptidase-M (CPM) is a membrane-bound peptidase that metabolizes peptides, and is present in pneumocytes. CPM hydrolyses the C-terminal arginine of epidermal growth factor (EGF) resulting in des-Arg53-EGF which binds to the EGF receptor (EGFR) with an equal or greater affinity than native EGF. Therefore, this study focused on the possible presence of CPM in human lung adenocarcinomas (ADC) and evaluated the relationship between CPM and EGFR by assessing the impact of expressions on patient clinical outcome.
Methods: This is a retrospective study of 110 patients who underwent resection of the primary tumour (92) or metastatic tissues (18) for treatment or diagnosis. Immunohistochemistry (IHC) for CPM and EGFR was made in serial sections using standard methods.
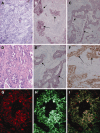
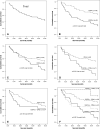
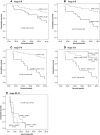
Results: This study demonstrates for the first time that 23.6% of ADCs express carboxypeptidase-M (26/110), mainly in membrane-bound forms. The amounts and the extent of CPM within tumours vary from low levels to obviously overexpressed forms. The immunohistochemical positivity (+) for CPM in ADCs negatively correlated with disease survival. In addition, 80% of CPM+ adenocarcinomas (21/26) showed a coexpression with EGFR suggesting a high prevalence for coexistence. The follow up data indicated a significantly shorter 5-year survival time for patients with CPM+-EGFR+ (double-positive) tumours compared to those harbouring neoplasias negative for both proteins (9.5 vs. 60.4% survivals, P < 0.001).
Conclusion: The fact that CPM+ ADCs often co-express with EGFR suggests a functional-regulatory link between these proteins which might have therapeutical consequences. The present novel data could lead to improved IHC tests in lung adenocarcinomas for EGFR expression.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Comparison of Two Modern Survival Prediction Tools, SORG-MLA and METSSS, in Patients With Symptomatic Long-bone Metastases Who Underwent Local Treatment With Surgery Followed by Radiotherapy and With Radiotherapy Alone.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2024 Dec 1;482(12):2193-2208. doi: 10.1097/CORR.0000000000003185. Epub 2024 Jul 23. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2024. PMID: 39051924
-
First-line treatment of advanced epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) mutation positive non-squamous non-small cell lung cancer.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016 May 25;(5):CD010383. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010383.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Mar 18;3:CD010383. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010383.pub3. PMID: 27223332 Updated.
-
International association for the study of lung cancer/american thoracic society/european respiratory society international multidisciplinary classification of lung adenocarcinoma.J Thorac Oncol. 2011 Feb;6(2):244-85. doi: 10.1097/JTO.0b013e318206a221. J Thorac Oncol. 2011. PMID: 21252716 Free PMC article.
-
A rapid and systematic review of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of paclitaxel, docetaxel, gemcitabine and vinorelbine in non-small-cell lung cancer.Health Technol Assess. 2001;5(32):1-195. doi: 10.3310/hta5320. Health Technol Assess. 2001. PMID: 12065068
-
The role of EGF-R expression on patient survival in lung cancer: a systematic review with meta-analysis.Eur Respir J. 2002 Oct;20(4):975-81. doi: 10.1183/09031936.02.00296502. Eur Respir J. 2002. PMID: 12412692
Cited by
-
Analyses of association between PPAR gamma and EPHX1 polymorphisms and susceptibility to COPD in a Hungarian cohort, a case-control study.BMC Med Genet. 2010 Nov 2;11:152. doi: 10.1186/1471-2350-11-152. BMC Med Genet. 2010. PMID: 21044285 Free PMC article.
-
Genomic landscape of liposarcoma.Oncotarget. 2015 Dec 15;6(40):42429-44. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.6464. Oncotarget. 2015. PMID: 26643872 Free PMC article.
-
Discovery of lung cancer biomarkers by profiling the plasma proteome with monoclonal antibody libraries.Mol Cell Proteomics. 2011 Dec;10(12):M111.010298. doi: 10.1074/mcp.M111.010298. Epub 2011 Sep 26. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2011. PMID: 21947365 Free PMC article.
-
Minireview: functional roles of tissue kallikrein, kinins, and kallikrein-related peptidases in lung cancer.Med Oncol. 2023 Jul 5;40(8):224. doi: 10.1007/s12032-023-02090-x. Med Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37405520 Review.
-
Mapping of carboxypeptidase m in normal human kidney and renal cell carcinoma: expression in tumor-associated neovasculature and macrophages.J Histochem Cytochem. 2013 Mar;61(3):218-35. doi: 10.1369/0022155412470456. Epub 2012 Nov 19. J Histochem Cytochem. 2013. PMID: 23172796 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Blanco-Aparicio C, Molina MA, Fernandez-Salas E et al (1998) Potato carboxypeptidase inhibitor, a T-knot protein is an epidermal growth factor antagonist that inhibits tumor cell growth. J Biol Chem 273:12370–12377 - PubMed
-
- Brambilla E, Travis WD, Colby TV, Corrin B Shimosato Y (2001) Histologic typing of tumours of lung and pleura: the new World Health Organization classification of tumours. Eur Respir J 18:1059–1068 - PubMed
-
- Ciardiello F (2005) Epidermal growth factor receptor inhibitors in cancer treatment. Future Oncol 1:221–234 - PubMed
-
- Cohen AJ, Skidgel RA, Gilman LB et al (1997) Carboxypeptidase M: variable expression in normal human lung and inactivation in lung cancer. Chest 11:149S - PubMed
-
- Dacic S, Flanagan M, Cieply K et al (2006) Significance of EGFR protein expression and gene amplification in non-small cell lung carcinoma. Am J Clin Pathol 125:860–865 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

