The reliability of the Vernon and Mior neck disability index, and its validity compared with the short form-36 health survey questionnaire
- PMID: 17922152
- PMCID: PMC2140132
- DOI: 10.1007/s00586-007-0503-y
The reliability of the Vernon and Mior neck disability index, and its validity compared with the short form-36 health survey questionnaire
Abstract
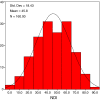
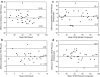
Prospective single cohort study. To evaluate the NDI by comparison with the SF36 health Survey Questionnaire. The NDI is a simple ten-item questionnaire used to assess patients with neck pain. The SF36 measures functional ability, well being and the overall health of patients. It is used as a gold standard in health economics to assess the health utility, gain and economic impact of medical interventions. One hundred and sixty patients with neck pain attending the spinal clinic completed self-assessment questionnaires. A second questionnaire was completed in 34 patients after a period of 1-2 weeks. The internal consistency of the NDI and SF36 was calculated using Cronbach's alpha. The test-retest reliability was assessed using the Bland and Altman method. The concurrent validity of the NDI with respect to the SF-36 was assessed using Pearson correlations. Both questionnaires showed robust internal consistency: Cronbach's alpha for the NDI scale was acceptable (0.864, 95% confidence limits 0.825-0.894) though slightly smaller than that of the SF36. The correlations between each item of the NDI scores and the total NDI score ranged from 0.447 to 0.659, (all with P < 0.001). The test-retest reliability of the NDI was high (intra-class correlation 0.93, 95% confidence limits 0.86-0.97) and comparable with the best values found for SF36. The correlations between NDI and SF36 domains ranged from -0.45 to -0.74 (all with P < 0.001). We have shown that the NDI has good reliability and validity and that it compares well with the SF36 in the spinal surgery out patient setting.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Neck Pain and Disability Scale and Neck Disability Index: validity of Dutch language versions.Eur Spine J. 2012 Jan;21(1):93-100. doi: 10.1007/s00586-011-1920-5. Epub 2011 Aug 4. Eur Spine J. 2012. PMID: 21814745 Free PMC article.
-
Cross-cultural adaptation of the Neck Disability Index and Copenhagen Neck Functional Disability Scale for patients with neck pain due to degenerative and discopathic disorders. Psychometric properties of the Polish versions.BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2011 Apr 29;12:84. doi: 10.1186/1471-2474-12-84. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2011. PMID: 21529360 Free PMC article.
-
Validation of the Neck Disability Index in Serbian Patients With Cervical Radiculopathy.J Manipulative Physiol Ther. 2018 Jul-Aug;41(6):496-502. doi: 10.1016/j.jmpt.2017.10.018. Epub 2018 Aug 11. J Manipulative Physiol Ther. 2018. PMID: 30107938
-
The Short-Form Neck Disability index has adequate measurement properties in chronic neck pain patients.Eur Spine J. 2021 Dec;30(12):3593-3599. doi: 10.1007/s00586-021-07019-4. Epub 2021 Oct 14. Eur Spine J. 2021. PMID: 34647181 Free PMC article.
-
Patient-Reported Outcome Measures Used for Neck Disorders: An Overview of Systematic Reviews.J Orthop Sports Phys Ther. 2018 Oct;48(10):775-788. doi: 10.2519/jospt.2018.8131. Epub 2018 Jun 22. J Orthop Sports Phys Ther. 2018. PMID: 29932874
Cited by
-
Criteria for determining if a treatment for pain works.Interv Pain Med. 2022 Aug 15;1(Suppl 2):100125. doi: 10.1016/j.inpm.2022.100125. eCollection 2022. Interv Pain Med. 2022. PMID: 39239124 Free PMC article.
-
C1 lateral mass screw placement with intentional sacrifice of the C2 ganglion: functional outcomes and morbidity in elderly patients.Eur Spine J. 2010 Aug;19(8):1318-24. doi: 10.1007/s00586-010-1452-4. Epub 2010 May 22. Eur Spine J. 2010. PMID: 20496037 Free PMC article.
-
The association between neck pain, the Neck Disability Index and cervical ranges of motion: a narrative review.J Can Chiropr Assoc. 2011 Sep;55(3):211-21. J Can Chiropr Assoc. 2011. PMID: 21886283 Free PMC article.
-
Prevalence and Characteristics of Chronic Spinal Pain Patients with Different Hopes (Treatment Goals) for Ongoing Chiropractic Care.J Altern Complement Med. 2019 Oct;25(10):1015-1025. doi: 10.1089/acm.2019.0247. Epub 2019 Aug 27. J Altern Complement Med. 2019. PMID: 31453711 Free PMC article.
-
The interrater reliability of a pain mechanisms-based classification for patients with nonspecific neck pain.Braz J Phys Ther. 2019 Sep-Oct;23(5):437-447. doi: 10.1016/j.bjpt.2018.10.008. Epub 2018 Oct 29. Braz J Phys Ther. 2019. PMID: 30389348 Free PMC article.
References
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'DOI', 'value': '10.1080/165019702760390383', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://doi.org/10.1080/165019702760390383'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '12440803', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12440803/'}]}
- Ackelman BH, Lindgren U (2002) Validity and reliability of a modified version of the neck disability index. J Rehabil Med 34:284–287 - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'PMC', 'value': 'PMC2352101', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC2352101/'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '8819450', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/8819450/'}]}
- Bland JM, Altman DG (1996) Measurement error. Br Med J 313:744–746 - PMC - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'PMC', 'value': 'PMC2126061', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC2126061/'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '9055718', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/9055718/'}]}
- Bland JM, Altman DG (1997) Statistics notes: Cronbach’s alpha. BMJ 314:572 - PMC - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '8066508', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/8066508/'}]}
- Bovim G, Schrader H, Sand T (1994) Neck pain in the general population. Spine 19:1307–1309 - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'DOI', 'value': '10.1097/01.brs.0000201241.90914.22', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://doi.org/10.1097/01.brs.0000201241.90914.22'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '16508559', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16508559/'}]}
- Cleland JA, Fritz JM, Whitman JM, Palmer JA (2006) The reliability and construct validity of the neck disability index and patient specific functional scale in patients with cervical radiculopathy. Spine 31:598–602 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical