A global analysis of NMR distance constraints from the PDB
- PMID: 17922259
- PMCID: PMC2048825
- DOI: 10.1007/s10858-007-9199-x
A global analysis of NMR distance constraints from the PDB
Abstract
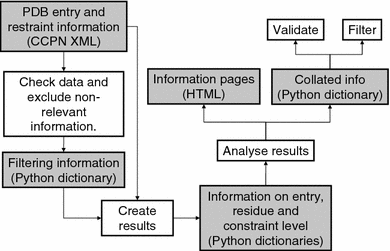
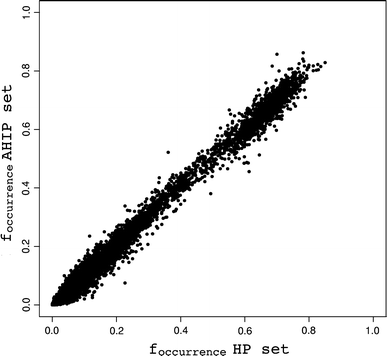
Information obtained from Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) experiments is encoded as a set of constraint lists when calculating three-dimensional structures for a protein. With the amount of constraint data from the world wide Protein Data Bank (wwPDB) that is now available, it is possible to do a global, large-scale analysis using only information from the constraints, without taking the coordinate information into account. This article describes such an analysis of distance constraints from NOE data based on a set of 1834 NMR PDB entries containing 1909 protein chains. In order to best represent the quality and extent of the data that is currently deposited at the wwPDB, only the original data as deposited by the authors was used, and no attempt was made to 'clean up' and further interpret this information. Because the constraint lists provide a single set of data, and not an ensemble of structural solutions, they are easier to analyse and provide a reduced form of structural information that is relevant for NMR analysis only. The online resource resulting from this analysis ( http://www.ebi.ac.uk/msd/srv/docs/NMR/analysis/results/html/comparison.html ) makes it possible to check, for example, how often a particular contact occurs when assigning NOESY spectra, or to find out whether a particular sequence fragment is likely to be difficult to assign. In this respect it formalises information that scientists with experience in spectrum analysis are aware of but cannot necessarily quantify. The analysis described here illustrates the importance of depositing constraints (and all other possible NMR derived information) along with the structure coordinates, as this type of information can greatly assist the NMR community.
Figures



Similar articles
-
BioMagResBank database with sets of experimental NMR constraints corresponding to the structures of over 1400 biomolecules deposited in the Protein Data Bank.J Biomol NMR. 2003 Jun;26(2):139-46. doi: 10.1023/a:1023514106644. J Biomol NMR. 2003. PMID: 12766409
-
Protein NMR structure determination with automated NOE assignment using the new software CANDID and the torsion angle dynamics algorithm DYANA.J Mol Biol. 2002 May 24;319(1):209-27. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(02)00241-3. J Mol Biol. 2002. PMID: 12051947
-
BioMagResBank (BMRB) as a Resource for Structural Biology.Methods Mol Biol. 2020;2112:187-218. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-0270-6_14. Methods Mol Biol. 2020. PMID: 32006287 Free PMC article.
-
The Protein Data Bank Archive.Methods Mol Biol. 2021;2305:3-21. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-1406-8_1. Methods Mol Biol. 2021. PMID: 33950382 Review.
-
Quality assessment of protein NMR structures.Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2013 Oct;23(5):715-24. doi: 10.1016/j.sbi.2013.08.005. Epub 2013 Sep 21. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2013. PMID: 24060334 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The NMR restraints grid at BMRB for 5,266 protein and nucleic acid PDB entries.J Biomol NMR. 2009 Dec;45(4):389-96. doi: 10.1007/s10858-009-9378-z. Epub 2009 Oct 7. J Biomol NMR. 2009. PMID: 19809795 Free PMC article.
-
Straightforward and complete deposition of NMR data to the PDBe.J Biomol NMR. 2010 Oct;48(2):85-92. doi: 10.1007/s10858-010-9439-3. Epub 2010 Aug 3. J Biomol NMR. 2010. PMID: 20680401 Free PMC article.
-
The Protein Data Bank in Europe (PDBe): bringing structure to biology.Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr. 2011 Apr;67(Pt 4):324-30. doi: 10.1107/S090744491004117X. Epub 2011 Mar 18. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr. 2011. PMID: 21460450 Free PMC article.
-
PDBe: Protein Data Bank in Europe.Nucleic Acids Res. 2010 Jan;38(Database issue):D308-17. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkp916. Epub 2009 Oct 25. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010. PMID: 19858099 Free PMC article.
-
NRG-CING: integrated validation reports of remediated experimental biomolecular NMR data and coordinates in wwPDB.Nucleic Acids Res. 2012 Jan;40(Database issue):D519-24. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkr1134. Epub 2011 Dec 1. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012. PMID: 22139937 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bates D, Chambers J, Dalgaard P et al (2007) The R project for statistical computing. http://www.r-project.org/. Cited 10 Apr 2006. University site
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'DOI', 'value': '10.1093/nar/gkl971', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkl971'}, {'type': 'PMC', 'value': 'PMC1669775', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC1669775/'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '17142228', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17142228/'}]}
- Berman H, Henrick K, Nakamura H et al (2007) The worldwide Protein Data Bank (wwPDB): ensuring a single uniform archive of PDB data. Nucleic Acids Res 35:D301–D303 - PMC - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'DOI', 'value': '10.1006/jmbi.1998.1808', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://doi.org/10.1006/jmbi.1998.1808'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '9680482', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/9680482/'}]}
- Doreleijers JF, Rullmann JA, Kaptein R (1998) Quality assessment of NMR structures: a statistical survey. J Mol Biol 281:149–164 - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'DOI', 'value': '10.1023/A:1023514106644', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://doi.org/10.1023/a:1023514106644'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '12766409', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12766409/'}]}
- Doreleijers JF, Mading S, Maziuk D et al (2003) BioMagResBank database with sets of experimental NMR constraints corresponding to the structures of over 1400 biomolecules deposited in the Protein Data Bank. J Biomol NMR 26:139–146 - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'DOI', 'value': '10.1007/s10858-005-2195-0', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://doi.org/10.1007/s10858-005-2195-0'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '16041478', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16041478/'}]}
- Doreleijers JF, Nederveen AJ, Vranken W et al (2005) BioMagResBank databases DOCR and FRED containing converted and filtered sets of experimental NMR restraints and coordinates from over 500 protein PDB structures. J Biomol NMR 32:1–12 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

