Bactericidal action of daptomycin against stationary-phase and nondividing Staphylococcus aureus cells
- PMID: 17923487
- PMCID: PMC2167999
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.00824-07
Bactericidal action of daptomycin against stationary-phase and nondividing Staphylococcus aureus cells
Abstract
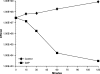
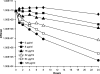
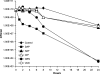
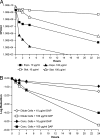
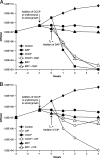
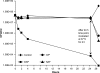
Most antibiotics with bactericidal activity require that the bacteria be actively dividing to produce rapid killing. However, in many infections, such as endocarditis, prosthetic joint infections, and infected embedded catheters, the bacteria divide slowly or not at all. Daptomycin is a lipopeptide antibiotic with a distinct mechanism of action that targets the cytoplasmic membrane of gram-positive organisms, including Staphylococcus aureus. Daptomycin is rapidly bactericidal against exponentially growing bacteria (a 3-log reduction in 60 min). The objectives of this study were to determine if daptomycin is bactericidal against nondividing S. aureus and to quantify the extent of the bactericidal activity. In high-inoculum methicillin-sensitive S. aureus cultures in stationary phase (10(10) CFU/ml), daptomycin displayed concentration-dependent bactericidal activity, requiring 32 micro/ml to achieve a 3-log reduction. In a study comparing several antibiotics at 100 microg/ml, daptomycin demonstrated faster bactericidal activity than nafcillin, ciprofloxacin, gentamicin, and vancomycin. In experiments where bacterial cell growth was halted by the metabolic inhibitor carbonyl cyanide m-chlorophenylhydrazone or erythromycin, daptomycin (10 microg/ml) achieved the bactericidal end point (a 3-log reduction) within 2 h. In contrast, ciprofloxacin (10 microg/ml) did not produce bactericidal activity. Daptomycin (2 microg/ml) remained bactericidal against cold-arrested S. aureus, which was protected from the actions of ciprofloxacin and nafcillin. The data presented here suggest that, in contrast to that of other classes of antibiotics, the bactericidal activity of daptomycin does not require cell division or active metabolism, most likely as a consequence of its direct action on the bacterial membrane.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Impact of high-inoculum Staphylococcus aureus on the activities of nafcillin, vancomycin, linezolid, and daptomycin, alone and in combination with gentamicin, in an in vitro pharmacodynamic model.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2004 Dec;48(12):4665-72. doi: 10.1128/AAC.48.12.4665-4672.2004. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2004. PMID: 15561842 Free PMC article.
-
Short-course gentamicin in combination with daptomycin or vancomycin against Staphylococcus aureus in an in vitro pharmacodynamic model with simulated endocardial vegetations.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2005 Jul;49(7):2735-45. doi: 10.1128/AAC.49.7.2735-2745.2005. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2005. PMID: 15980344 Free PMC article.
-
Rapid bactericidal activity of daptomycin against methicillin-resistant and methicillin-susceptible Staphylococcus aureus peritonitis in mice as measured with bioluminescent bacteria.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2007 May;51(5):1787-94. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00738-06. Epub 2007 Feb 16. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2007. PMID: 17307984 Free PMC article.
-
A current perspective on daptomycin for the clinical microbiologist.Clin Microbiol Rev. 2013 Oct;26(4):759-80. doi: 10.1128/CMR.00030-13. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2013. PMID: 24092854 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The efficacy and safety of daptomycin: first in a new class of antibiotics for Gram-positive bacteria.Clin Microbiol Infect. 2006 Mar;12 Suppl 1:24-32. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-0691.2006.01342.x. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2006. PMID: 16445721 Review.
Cited by
-
Pneumococcal competence is a populational health sensor driving multilevel heterogeneity in response to antibiotics.Nat Commun. 2024 Jul 10;15(1):5625. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-49853-2. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 38987237 Free PMC article.
-
Distinguishing between resistance, tolerance and persistence to antibiotic treatment.Nat Rev Microbiol. 2016 Apr;14(5):320-30. doi: 10.1038/nrmicro.2016.34. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2016. PMID: 27080241 Review.
-
New Insight into Daptomycin Bioavailability and Localization in Staphylococcus aureus Biofilms by Dynamic Fluorescence Imaging.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2016 Jul 22;60(8):4983-90. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00735-16. Print 2016 Aug. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2016. PMID: 27297479 Free PMC article.
-
Catalase Protects Biofilm of Staphylococcus aureus against Daptomycin Activity.Antibiotics (Basel). 2021 Apr 30;10(5):511. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics10050511. Antibiotics (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33946290 Free PMC article.
-
Daptomycin therapy for osteomyelitis: a retrospective study.BMC Infect Dis. 2012 Jun 12;12:133. doi: 10.1186/1471-2334-12-133. BMC Infect Dis. 2012. PMID: 22691420 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

