Voriconazole inhibits melanization in Cryptococcus neoformans
- PMID: 17923488
- PMCID: PMC2167997
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.00376-07
Voriconazole inhibits melanization in Cryptococcus neoformans
Abstract
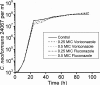
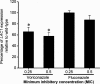
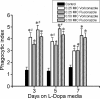
Voriconazole is a triazole antifungal drug that inhibits ergosterol synthesis and has broad activity against yeast and molds. While studying the interaction of voriconazole and Cryptococcus neoformans, we noted that cells grown in the presence of subinhibitory concentrations of voriconazole reduced melanin pigmentation. We investigated this effect systematically by assessing melanin production in the presence of voriconazole, amphotericin B, caspofungin, itraconazole, and fluconazole. Only voriconazole impeded the formation of melanin at subinhibitory concentrations. Voriconazole did not affect the autopolymerization of l-dopa, and 0.5 MIC of voriconazole did affect the gene expression of C. neoformans. However, voriconazole inhibited the capacity of laccase to catalyze the formation of melanin. Hence, voriconazole affects melanization in C. neoformans by interacting directly with laccase, which may increase the efficacy of this potent antifungal against certain pigmented fungi.
Figures


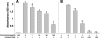
Similar articles
-
Effects of voriconazole on Cryptococcus neoformans.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2004 Jun;48(6):2014-20. doi: 10.1128/AAC.48.6.2014-2020.2004. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2004. PMID: 15155193 Free PMC article.
-
Melanization of Cryptococcus neoformans and Histoplasma capsulatum reduces their susceptibilities to amphotericin B and caspofungin.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2002 Nov;46(11):3394-400. doi: 10.1128/AAC.46.11.3394-3400.2002. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2002. PMID: 12384341 Free PMC article.
-
Susceptibility of Cryptococcus neoformans biofilms to antifungal agents in vitro.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2006 Mar;50(3):1021-33. doi: 10.1128/AAC.50.3.1021-1033.2006. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2006. PMID: 16495265 Free PMC article.
-
[Melanin and its role on the virulence of Cryptococcus neoformans].Mikrobiyol Bul. 2010 Jul;44(3):519-26. Mikrobiyol Bul. 2010. PMID: 21064003 Review. Turkish.
-
Fungal melanin-induced metabolic reprogramming in macrophages is crucial for inflammation.J Mycol Med. 2023 May;33(2):101359. doi: 10.1016/j.mycmed.2023.101359. Epub 2023 Jan 16. J Mycol Med. 2023. PMID: 36701872 Review.
Cited by
-
The biofilm produced by Cryptococcus neoformans protects the fungus from the antifungal and anti-melanin effects of cyclosporine.Microb Pathog. 2025 Jan;198:107124. doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2024.107124. Epub 2024 Nov 15. Microb Pathog. 2025. PMID: 39551108
-
Ptilomycalin A inhibits laccase and melanization in Cryptococcus neoformans.Bioorg Med Chem. 2011 Nov 15;19(22):6654-7. doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2011.05.041. Epub 2011 May 27. Bioorg Med Chem. 2011. PMID: 21715177 Free PMC article.
-
Combination efficacy of voriconazole and amphotericin B in the experimental disease in immunodeficient mice caused by fluconazole-resistant Cryptococcus neoformans.Mycopathologia. 2011 Apr;171(4):261-6. doi: 10.1007/s11046-010-9375-5. Epub 2010 Oct 24. Mycopathologia. 2011. PMID: 20972836
-
Assessment of efficacy of antifungals against Aspergillus fumigatus: value of real-time bioluminescence imaging.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2013 Jul;57(7):3046-59. doi: 10.1128/AAC.01660-12. Epub 2013 Apr 15. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2013. PMID: 23587947 Free PMC article.
-
Investigation of the influence of pH and temperature on melanization and survival under oxidative stress in Cryptococcus neoformans.Arch Microbiol. 2024 Jul 17;206(8):355. doi: 10.1007/s00203-024-04080-7. Arch Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 39017938
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R21 GM071421/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI033774/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI056070/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- HL059842/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI052733/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI052733/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R37 AI033142/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- GM-071421/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- AI056070-01A2/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI033142/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI52733/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AI051519/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL059842/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- AI-51519/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI033142/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI033774/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

