Two regulatory steps of ER-stress sensor Ire1 involving its cluster formation and interaction with unfolded proteins
- PMID: 17923530
- PMCID: PMC2064738
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.200704166
Two regulatory steps of ER-stress sensor Ire1 involving its cluster formation and interaction with unfolded proteins
Abstract
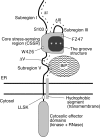
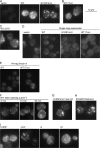
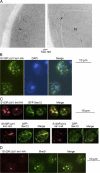
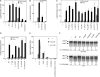
Chaperone protein BiP binds to Ire1 and dissociates in response to endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress. However, it remains unclear how the signal transducer Ire1 senses ER stress and is subsequently activated. The crystal structure of the core stress-sensing region (CSSR) of yeast Ire1 luminal domain led to the controversial suggestion that the molecule can bind to unfolded proteins. We demonstrate that, upon ER stress, Ire1 clusters and actually interacts with unfolded proteins. Ire1 mutations that affect these phenomena reveal that Ire1 is activated via two steps, both of which are ER stress regulated, albeit in different ways. In the first step, BiP dissociation from Ire1 leads to its cluster formation. In the second step, direct interaction of unfolded proteins with the CSSR orients the cytosolic effector domains of clustered Ire1 molecules.
Figures



Similar articles
-
BiP binding to the ER-stress sensor Ire1 tunes the homeostatic behavior of the unfolded protein response.PLoS Biol. 2010 Jul 6;8(7):e1000415. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.1000415. PLoS Biol. 2010. PMID: 20625545 Free PMC article.
-
BiP-bound and nonclustered mode of Ire1 evokes a weak but sustained unfolded protein response.Genes Cells. 2013 Apr;18(4):288-301. doi: 10.1111/gtc.12035. Epub 2013 Feb 6. Genes Cells. 2013. PMID: 23387983
-
Unfolded proteins are Ire1-activating ligands that directly induce the unfolded protein response.Science. 2011 Sep 30;333(6051):1891-4. doi: 10.1126/science.1209126. Epub 2011 Aug 18. Science. 2011. PMID: 21852455 Free PMC article.
-
How IRE1 reacts to ER stress.Cell. 2008 Jan 11;132(1):24-6. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2007.12.017. Cell. 2008. PMID: 18191217 Review.
-
Multiple Ways for Stress Sensing and Regulation of the Endoplasmic Reticulum-stress Sensors.Cell Struct Funct. 2021 May 22;46(1):37-49. doi: 10.1247/csf.21015. Epub 2021 Mar 26. Cell Struct Funct. 2021. PMID: 33775971 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Autonomous translational pausing is required for XBP1u mRNA recruitment to the ER via the SRP pathway.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016 Oct 4;113(40):E5886-E5895. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1604435113. Epub 2016 Sep 20. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016. PMID: 27651490 Free PMC article.
-
Proinsulin misfolding and endoplasmic reticulum stress during the development and progression of diabetes.Mol Aspects Med. 2015 Apr;42:105-18. doi: 10.1016/j.mam.2015.01.001. Epub 2015 Jan 8. Mol Aspects Med. 2015. PMID: 25579745 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Endoplasmic reticulum stress and lipid metabolism: mechanisms and therapeutic potential.Biochem Res Int. 2012;2012:841362. doi: 10.1155/2012/841362. Epub 2011 Dec 13. Biochem Res Int. 2012. PMID: 22195283 Free PMC article.
-
Yeast Heterologous Expression Systems for the Study of Plant Membrane Proteins.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jun 28;24(13):10768. doi: 10.3390/ijms241310768. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37445944 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Structural and mutational analysis of the ribosome-arresting human XBP1u.Elife. 2019 Jun 27;8:e46267. doi: 10.7554/eLife.46267. Elife. 2019. PMID: 31246176 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bertolotti, A., Y. Zhang, L.M. Hendershot, H.P. Harding, and D. Ron. 2000. Dynamic interaction of BiP and ER stress transducers in the unfolded-protein response. Nat. Cell Biol. 2:326–332. - PubMed
-
- Christianson, T.W., R.S. Sikorski, M. Dante, J.H. Shero, and P. Hieter. 1992. Multifunctional yeast high-copy-number shuttle vectors. Gene. 110:119–122. - PubMed
-
- Cox, J.S., and P. Walter. 1996. A novel mechanism for regulating activity of a transcription factor that controls the unfolded protein response. Cell. 87:391–404. - PubMed
-
- Cox, J.S., C.E. Shamu, and P. Walter. 1993. Transcriptional induction of genes encoding endoplasmic reticulum resident proteins requires a transmembrane protein kinase. Cell. 73:1197–1206. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

