Neuronal apoptosis inhibitory protein is overexpressed in patients with unfavorable prognostic factors in breast cancer
- PMID: 17923748
- PMCID: PMC2694398
- DOI: 10.3346/jkms.2007.22.S.S17
Neuronal apoptosis inhibitory protein is overexpressed in patients with unfavorable prognostic factors in breast cancer
Abstract
Neuronal apoptosis inhibitory protein (NAIP) is a recently identified inhibitor of apoptosis protein. However, the clinical relevance of NAIP expression is not completely understood. In an attempt to determine the clinical relevance of NAIP expression in breast cancer, the levels of NAIP and survivin expression were measured in 117 breast cancer samples and 10 normal breast tissues using quantitative reversetranscriptase-polymerase chain reaction. While there was no evidence of NAIP expression in the normal breast tissue, NAIP was expressed in all breast cancer samples. The level of NAIP expression in breast cancer was significantly higher (257 times) than in the universal tumor control. There was a strong correlation between the level of NAIP expression and the level of survivin expression (p=0.001). The level of NAIP expression in patients with a large tumor (>/=T2) and patients with an unfavorable histology (nuclear grade III) was significantly higher than in those patients with a small tumor (T1) and patients with a favorable histology (nuclear grade I, II) (p=0.026 and p=0.050, respectively). Although the level of NAIP expression was higher in patients with other unfavorable prognostic factors, it was not significant. The three-year relapse-free survival rate was not significantly the patients showing high NAIP expression and patients showing low NAIP expression (86.47plusmn;4.79% vs. 78.74plusmn;6.57%). Further studies should include the expressions of NAIP in a larger number of patients and for a longer period of follow-up to evaluate correlation with metastasis and treatment outcome. In conclusion, NAIP is overexpressed in breast cancer patients with unfavorable clinical features such as stage and tumor size, suggesting that NAIP would play a role in the disease manifestation.
Figures
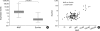

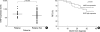
Similar articles
-
Survivin expression predicts early recurrence in early-stage breast cancer.Anticancer Res. 2007 Jul-Aug;27(4C):2803-8. Anticancer Res. 2007. PMID: 17695451
-
Expression of IAP family proteins in colon cancers from patients with different age groups.Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2004 Sep;53(9):770-6. doi: 10.1007/s00262-004-0534-8. Epub 2004 May 11. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2004. PMID: 15138717 Free PMC article.
-
Lack of prognostic significance of survivin, survivin-deltaEx3, survivin-2B, galectin-3, bag-1, bax-alpha and MRP-1 mRNAs in breast cancer.Cancer Lett. 2003 Nov 25;201(2):225-36. doi: 10.1016/s0304-3835(03)00518-4. Cancer Lett. 2003. PMID: 14607338
-
High survivin mRNA expression is a predictor of poor prognosis in breast cancer: a comparative study at the mRNA and protein level.Breast Cancer. 2014 Jul;21(4):482-90. doi: 10.1007/s12282-012-0403-9. Epub 2012 Sep 12. Breast Cancer. 2014. PMID: 22968628
-
Do the survivin (BIRC5) splice variants modulate or add to the prognostic value of total survivin in breast cancer?Clin Chem. 2006 Sep;52(9):1693-700. doi: 10.1373/clinchem.2006.071613. Epub 2006 Jul 27. Clin Chem. 2006. PMID: 16873289
Cited by
-
A Mouse-Specific Model to Detect Genes under Selection in Tumors.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Oct 26;15(21):5156. doi: 10.3390/cancers15215156. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37958330 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutic potential of a novel prodrug of green tea extract in induction of apoptosis via ERK/JNK and Akt signaling pathway in human endometrial cancer.BMC Cancer. 2020 Oct 6;20(1):964. doi: 10.1186/s12885-020-07455-3. BMC Cancer. 2020. PMID: 33023525 Free PMC article.
-
Double gene siRNA knockdown of mutant p53 and TNF induces apoptosis in triple-negative breast cancer cells.Onco Targets Ther. 2016 Nov 11;9:6921-6933. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S110719. eCollection 2016. Onco Targets Ther. 2016. PMID: 27956838 Free PMC article.
-
Role of IAPs in prostate cancer progression: immunohistochemical study in normal and pathological (benign hyperplastic, prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia and cancer) human prostate.BMC Cancer. 2010 Jan 15;10:18. doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-10-18. BMC Cancer. 2010. PMID: 20078866 Free PMC article.
-
NLR-regulated pathways in cancer: opportunities and obstacles for therapeutic interventions.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2016 May;73(9):1741-64. doi: 10.1007/s00018-015-2123-8. Epub 2015 Dec 26. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2016. PMID: 26708292 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Reed CJ. Apoptosis and cancer: strategies for integrating programmed cell death. Semin Hematol. 2000;37(4 Suppl 7):9–16. - PubMed
-
- Ikeguchi M, Kaibara N. Changes in survivin messenger RNA level during cisplatin treatment in gastric cancer. Int J Mol Med. 2001;8:661–666. - PubMed
-
- Herr I, Debatin KM. Cellular stress response and apoptosis in cancer therapy. Blood. 2001;98:2603–2614. - PubMed
-
- Kawasaki H, Toyoda M, Shinohara H, Okuda J, Watanabe I, Yamamoto T, Tanaka K, Tenjo T, Tanigawa N. Expression of survivin correlates with apoptosis, proliferation, and angiogenesis during human colorectal tumorigenesis. Cancer. 2001;91:2026–2032. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

