Childhood central nervous system leukemia: historical perspectives, current therapy, and acute neurological sequelae
- PMID: 17924103
- PMCID: PMC2386669
- DOI: 10.1007/s00234-007-0300-7
Childhood central nervous system leukemia: historical perspectives, current therapy, and acute neurological sequelae
Abstract
Introduction: During the past three decades, improvements in the treatment of childhood leukemia have resulted in high cure rates, particularly for acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL). Unfortunately, successful therapy has come with a price, as significant morbidity can result from neurological affects which harm the brain and spinal cord. The expectation and hope is that chemotherapy, as a primary means of CNS therapy, will result in acceptable disease control with less CNS morbidity than has been observed with combinations of chemotherapy and radiotherapy over the past several decades.
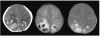
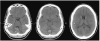
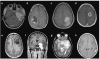
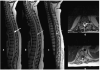
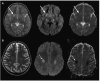
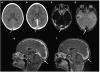
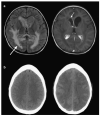
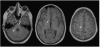
Methods and results: In this review we discuss the poignant, historical aspects of CNS leukemia therapy, outline current methods of systemic and CNS leukemia therapy, and present imaging findings we have encountered in childhood leukemia patients with a variety of acute neurological conditions. A major objective of our research is to understand the neuroimaging correlates of acute and chronic effects of cancer and therapy. Specific features related to CNS leukemia and associated short-term toxicities, both disease- and therapy-related, are emphasized in this review with the specific neuroimaging findings. Specific CNS findings are similarly important when treating acute myelogenous leukemia (AML), and details of leukemic involvement and toxicities are also presented in this entity.
Conclusion: Despite contemporary treatment approaches which favor the use of chemotherapy (including intrathecal therapy) over radiotherapy in the treatment of CNS leukemia, children still occasionally experience morbid neurotoxicity. Standard neuroimaging is sufficient to identify a variety of neurotoxic sequelae in children, and often suggest specific etiologies. Specific neuroimaging findings frequently indicate a need to alter antileukemia therapy. It is important to appreciate that intrathecal and high doses of systemic chemotherapy are not innocuous and are associated with acute, specific, recognizable, and often serious neurological consequences.
Figures

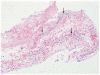
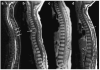
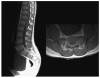
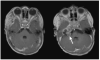

Similar articles
-
Risk and prognosis of central nervous system leukemia in patients with Philadelphia chromosome-positive acute leukemias treated with imatinib mesylate.Clin Cancer Res. 2003 Oct 15;9(13):4674-81. Clin Cancer Res. 2003. PMID: 14581336
-
Central nervous system involvement in adult acute lymphoblastic leukemia.Hematology. 2008 Oct;13(5):293-302. doi: 10.1179/102453308X343374. Hematology. 2008. PMID: 18854093 Review.
-
Central Nervous System Involvement in Adults with Acute Leukemia: Diagnosis, Prevention, and Management.Curr Oncol Rep. 2022 Apr;24(4):427-436. doi: 10.1007/s11912-022-01220-4. Epub 2022 Feb 10. Curr Oncol Rep. 2022. PMID: 35141858 Review.
-
Managing CNS disease in adults with acute lymphoblastic leukemia.Leuk Lymphoma. 2018 Jan;59(1):3-13. doi: 10.1080/10428194.2017.1326597. Epub 2017 May 23. Leuk Lymphoma. 2018. PMID: 28535095 Review.
-
Central nervous system involvement in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia: challenges and solutions.Leukemia. 2022 Dec;36(12):2751-2768. doi: 10.1038/s41375-022-01714-x. Epub 2022 Oct 20. Leukemia. 2022. PMID: 36266325 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Immunotherapy Associated Neurotoxicity in Pediatric Oncology.Front Oncol. 2022 Feb 21;12:836452. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.836452. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35265526 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Imaging of Central Nervous System Involvement in Pediatric Hematologic Disorders.Turk Arch Pediatr. 2022 May;57(3):267-281. doi: 10.5152/TurkArchPediatr.2022.22085. Turk Arch Pediatr. 2022. PMID: 35781229 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of genetic polymorphisms on chemotherapy toxicity in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia.Front Genet. 2012 Nov 22;3:249. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2012.00249. eCollection 2012. Front Genet. 2012. PMID: 23189085 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular Analysis of Central Nervous System Disease Spectrum in Childhood Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia.Clin Med Insights Oncol. 2016 Mar 14;10:5-15. doi: 10.4137/CMO.S18180. eCollection 2016. Clin Med Insights Oncol. 2016. PMID: 26997880 Free PMC article.
-
Adverse effects of treatment in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia: general overview and implications for long-term cardiac health.Expert Rev Hematol. 2011 Apr;4(2):185-97. doi: 10.1586/ehm.11.8. Expert Rev Hematol. 2011. PMID: 21495928 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Pui CH, Evans WE. Treatment of acute lymphoblastic leukemia. N Engl J Med. 2006;354:166–178. - PubMed
-
- Creutzig U, Zimmermann M, Ritter J, Reinhardt D, Hermann J, Henze G, Jurgens H, Kabisch H, Reiter A, Riehm H, Gadner H, Schellong G. Treatment strategies and long-term results in paediatric patients treated in four consecutive AML-BFM trials. Leukemia. 2005;19:2030–2042. - PubMed
-
- Gibson BE, Wheatley K, Hann IM, Stevens RF, Webb D, Hills RK, De Graaf SS, Harrison CJ. Treatment strategy and long-term results in paediatric patients treated in consecutive UK AML trials. Leukemia. 2005;19:2130–2138. - PubMed
-
- Pui CH, Cheng C, Leung W, Rai SN, Rivera GK, Sandlund JT, Ribeiro RC, Relling MV, Kun LE, Evans WE, Hudson MM. Extended follow-up of long-term survivors of childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia. N Engl J Med. 2003;349:640–649. - PubMed
-
- Kun LE. Leukemias in children. Pediatric Radiation Oncology. 2007:15–39.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

