The first genomewide interaction and locus-heterogeneity linkage scan in bipolar affective disorder: strong evidence of epistatic effects between loci on chromosomes 2q and 6q
- PMID: 17924339
- PMCID: PMC2265644
- DOI: 10.1086/521690
The first genomewide interaction and locus-heterogeneity linkage scan in bipolar affective disorder: strong evidence of epistatic effects between loci on chromosomes 2q and 6q
Abstract
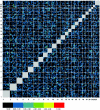
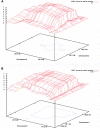
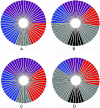
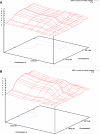
We present the first genomewide interaction and locus-heterogeneity linkage scan in bipolar affective disorder (BPAD), using a large linkage data set (52 families of European descent; 448 participants and 259 affected individuals). Our results provide the strongest interaction evidence between BPAD genes on chromosomes 2q22-q24 and 6q23-q24, which was observed symmetrically in both directions (nonparametric LOD [NPL] scores of 7.55 on 2q and 7.63 on 6q; P<.0001 and P=.0001, respectively, after a genomewide permutation procedure). The second-best BPAD interaction evidence was observed between chromosomes 2q22-q24 and 15q26. Here, we also observed a symmetrical interaction (NPL scores of 6.26 on 2q and 4.59 on 15q; P=.0057 and .0022, respectively). We covered the implicated regions by genotyping additional marker sets and performed a detailed interaction linkage analysis, which narrowed the susceptibility intervals. Although the heterogeneity analysis produced less impressive results (highest NPL score of 3.32) and a less consistent picture, we achieved evidence of locus heterogeneity at chromosomes 2q, 6p, 11p, 13q, and 22q, which was supported by adjacent markers within each region and by previously reported BPAD linkage findings. Our results provide systematic insights in the framework of BPAD epistasis and locus heterogeneity, which should facilitate gene identification by the use of more-comprehensive cloning strategies.
Figures
References
Web Resources
-
- deCODE Genetics, http://www.decode.com (for information about the genetic map)
-
- Institute for Medical Biometry, Informatics and Epidemiology, University of Bonn, http://mendel.meb.uni-bonn.de/~rfuerst/supplementary/ (for statistical programs used in the present study)
-
- NCBI, http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/ (for information about BPAD and the candidate genes)
-
- Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man (OMIM), http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Omim/ (for BPAD, TNFAIP6, NMI, TNFAIP3, IL20RA, IL22RA2, IFNGR1, BDNF, and DTNBP1)
-
- UCSC Genome Browser, http://genome.ucsc.edu/ (for information about the marker positions and RefSeq Genes track)
References
-
- Schumacher J, Kaneva R, Jamra RA, Diaz GO, Ohlraun S, Milanova V, Lee YA, Rivas F, Mayoral F, Fuerst R, et al (2005) Genomewide scan and fine-mapping linkage studies in four European samples with bipolar affective disorder suggest a new susceptibility locus on chromosome 1p35-p36 and provides further evidence of loci on chromosome 4q31 and 6q24. Am J Hum Genet 77:1102–1111 - PMC - PubMed
-
- American Psychiatric Association (1994) DSM-IV: diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders, 4th ed. American Psychiatric Association, Washington, DC
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

