De novo discovery of serotonin N-acetyltransferase inhibitors
- PMID: 17924613
- PMCID: PMC2531295
- DOI: 10.1021/jm0706463
De novo discovery of serotonin N-acetyltransferase inhibitors
Abstract
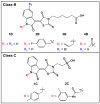
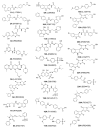
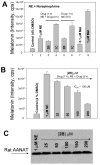
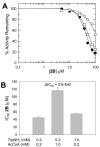
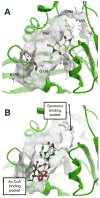
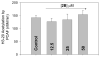
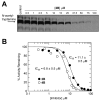
Serotonin N-acetyltransferase (arylalkylamine N-acetyltransferase, AANAT) is a member of the GCN5 N-acetyltransferase (GNAT) superfamily and catalyzes the penultimate step in the biosynthesis of melatonin; a large daily rhythm in AANAT activity drives the daily rhythm in circulating melatonin. We have used a structure-based computational approach to identify the first druglike and selective inhibitors of AANAT. Approximately 1.2 million compounds were virtually screened by 3D high-throughput docking into the active site of X-ray structures for AANAT, and in total 241 compounds were tested as inhibitors. One compound class, containing a rhodanine scaffold, exhibited low micromolar competitive inhibition against acetyl-CoA (AcCoA) and proved to be effective in blocking melatonin production in pineal cells. Compounds from this class are predicted to bind as bisubstrate inhibitors through interactions with the AcCoA and serotonin binding sites. Overall, this study demonstrates the feasibility of using virtual screening to identify small molecules that are selective inhibitors of AANAT.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Mechanistic studies on the alkyltransferase activity of serotonin N-acetyltransferase.Chem Biol. 2001 Apr;8(4):379-89. doi: 10.1016/s1074-5521(01)00020-5. Chem Biol. 2001. PMID: 11325593
-
Receptor- and ligand-based study on novel 2,2'-bithienyl derivatives as non-peptidic AANAT inhibitors.J Chem Inf Model. 2010 Mar 22;50(3):446-60. doi: 10.1021/ci9004805. J Chem Inf Model. 2010. PMID: 20196559
-
X-ray crystallographic studies of serotonin N-acetyltransferase catalysis and inhibition.J Mol Biol. 2002 Mar 22;317(2):215-24. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.2001.5371. J Mol Biol. 2002. PMID: 11902838
-
Homeobox genes and melatonin synthesis: regulatory roles of the cone-rod homeobox transcription factor in the rodent pineal gland.Biomed Res Int. 2014;2014:946075. doi: 10.1155/2014/946075. Epub 2014 Apr 30. Biomed Res Int. 2014. PMID: 24877149 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Serotonin N-acetyltransferase: mechanism and inhibition.Curr Med Chem. 2002 Jun;9(12):1187-99. doi: 10.2174/0929867023370013. Curr Med Chem. 2002. PMID: 12052171 Review.
Cited by
-
Structure of the disordered C terminus of Rab7 GTPase induced by binding to the Rab geranylgeranyl transferase catalytic complex reveals the mechanism of Rab prenylation.J Biol Chem. 2009 May 8;284(19):13185-92. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M900579200. Epub 2009 Feb 24. J Biol Chem. 2009. PMID: 19240028 Free PMC article.
-
Thiazolidinedione-based PI3Kα inhibitors: an analysis of biochemical and virtual screening methods.ChemMedChem. 2011 Mar 7;6(3):514-22. doi: 10.1002/cmdc.201000467. Epub 2011 Jan 4. ChemMedChem. 2011. PMID: 21360822 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting lysine acetylation readers and writers.Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2025 Feb;24(2):112-133. doi: 10.1038/s41573-024-01080-6. Epub 2024 Nov 21. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2025. PMID: 39572658 Review.
-
Evaluation of Rhodanine Indolinones as AANAT Inhibitors.ChemMedChem. 2024 Jan 2;19(1):e202300567. doi: 10.1002/cmdc.202300567. Epub 2023 Dec 6. ChemMedChem. 2024. PMID: 37984928 Free PMC article.
-
Synthesis of 1-(4-trifluoromethoxyphenyl)-2,5-dimethyl-3-(2-R-thiazol-4-yl)-1H-pyrroles via chain heterocyclization.Molecules. 2010 Feb 23;15(2):997-1006. doi: 10.3390/molecules15020997. Molecules. 2010. PMID: 20335958 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Arendt J. Melatonin and the Mammalian Pineal Gland. Chapman and Hall; London: 1995.
-
- Maestromi GJ, Conti A, Pierpaoli W. Role of the pineal gland in immunity. III. Melatonin antagonizes the immunosuppressive effect of acute stress via an opiatergic mechanism. Immunology. 1988;63:465–469. - PMC - PubMed
- Harlow HJ. Influence of the pineal gland and melatonin on blood flow and evaporative water loss during heat stress in rats. J Pineal Res. 1987;4:147–159. - PubMed
- Lewy AJ, Sack RL, Miller LS, Hoban TA. Antidepressant and circadian phase-shifting effects of light. Science. 1987;235:352–354. - PubMed
- Iguchi H, Kato K, Ibayashi H. Melatonin serum levels and metabolic clearance rate in patients with liver cirrhosis. J Clin Endocrin Metab. 1982;54:1025–1027. - PubMed
- Akerstedt T, Froberg JE, Friberg Y, Wetterberg L. Melatonin excretion, body temperature and subjective arousal during 64 hours of sleep deprivation. Psychoneuroendocrinology. 1979;4:219–225. - PubMed
- Cohen M, Lippman M, Chabner B. Role of pineal gland in aetiology and treatment of breast cancer. Lancet. 1978;ii:814–816. - PubMed
-
- Klein DC, Weller JL. Indole metabolism in the pineal gland: a circadian rhythm in N-acetyltransferase. Science. 1970;169:1093–1095. - PubMed
- Coon SL, Roseboom PH, Baler R, Weller JL, Namboodiri MAA, Koonin EV, Klein DC. Pineal serotonin N-acetyltransferase: expression cloning and molecular analysis. Science. 1995;270:1681–1683. - PubMed
- Borjigin J, Wang MM, Snyder SH. Diurnal variation in mRNA encoding serotonin N-acetyltransferase in pineal gland. Nature. 1995;378:783–785. - PubMed
- Klein DC, Roseboom PH, Coon SL. New light is shining on the melatonin rhythm enzyme. The first post-cloning view. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 1996;7:106–112. - PubMed
- Klein DC, Coon SL, Roseboom PH, Weller JL, Bernard M, Gastel JA, Zatz M, Iuvone PM, Rodriquez IR, Begay V, Falcon J, Cahil GM, Cassone VM, Baler R. The melatonin rhythm-generating enzyme: molecular regulation of serotonin N-acetyltransferase in the pineal gland. Recent Prog Hormone Res. 1997;52:307–357. - PubMed
- Klein DC. Arylalkylamine N-acetyltransferase: the Timezyme. J Biol Chem. 2007;282:4233–4237. - PubMed
-
- Boutin JA, Audinot V, Ferry G, Delagrange P. Molecular tools to study melatonin pathways and actions. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2005;26:412–419. - PubMed
- Ferry G, Ubeaud G, Mozo J, Pean C, Hennig P, Rodriguez M, Scoul C, Bonnaud A, Nosjean O, Galizzi JP, Delagrange P, Renard P, Volland JP, Yous S, Lesieur D, Boutin JA. New substrate analogues of human serotonin N-acetyltransferase produce in situ specific and potent inhibitors. Eur J Biochem. 2004;271:418–428. - PubMed
- Zheng W, Cole PA. Novel bisubstrate analog inhibitors of serotonin N-acetyltransferase: the importance of being neutral. Bioorg Chem. 2003;31:398–411. - PubMed
- Zheng W, Cole PA. Serotonin N-acetyltransferase: mechanism and inhibition. Curr Med Chem. 2002;9:1187–1199. - PubMed
- Beaurain N, Mesangeau C, Chavatte P, Ferry G, Audinot V, Boutin JA, Delagrange P, Bennejean C, Yous S. Design, synthesis and in vitro evaluation of novel derivatives as serotonin N-acetyltransferase inhibitors. J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 2002;17:409–414. - PubMed
- Ferry G, Loynel A, Kucharczyk N, Bertin S, Rodriguez M, Delagrange P, Galizzi JP, Jacoby E, Volland JP, Lesieur D, Renard P, Canet E, Fauchere JL, Boutin JA. Substrate Specificity and Inhibition Studies of Human Serotonin N-Acetyltransferase. J Biol Chem. 2000;275:8794–8805. - PubMed
- Kim CM, Cole PA. Bisubstrate ketone analogues as serotonin N-acetyltransferase inhibitors. J Med Chem. 2001;44:2479–2485. - PubMed
- Khalil EM, De Angelis J, Ishii M, Cole PA. Mechanism-based inhibition of the melatonin rhythm enzyme: pharmacologic exploitation of active site functional plasticity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1999;96:12418–12423. - PMC - PubMed
- Khalil EM, Cole PA. A Potent Inhibitor of the Melatonin Rhythm Enzyme. J Am Chem Soc. 1998;120:6195–6196.
- Robisaw JD, Neely JR. Coenzyme A metabolism. Am J Physiol. 1985;248:E1–9. - PubMed
- Lewczuk B, Zheng W, Prusik M, Cole PA, Przybylska-Gornowicz B. N-bromoacetyltryptamine strongly and reversibly inhibits in vitro melatonin secretion from mammalian pinealocytes. Neuro Endocrinol Lett. 2005;26:581–592. - PubMed
-
- De Angelis J, Gastel J, Klein DC, Cole PA. Kinetic analysis of the catalytic mechanism of serotonin N-acetyltransferase (EC 2.3.1.87) J Biol Chem. 1998;273:3045–3050. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Chemical Information

