Structural basis of disease-causing mutations in hepatocyte nuclear factor 1beta
- PMID: 17924661
- PMCID: PMC2367142
- DOI: 10.1021/bi7010527
Structural basis of disease-causing mutations in hepatocyte nuclear factor 1beta
Abstract
HNF1beta is an atypical POU transcription factor that participates in a hierarchical network of transcription factors controlling the development and proper function of vital organs such as liver, pancreas, and kidney. Many inheritable mutations on HNF1beta are the monogenic causes of diabetes and several kidney diseases. To elucidate the molecular mechanism of its function and the structural basis of mutations, we have determined the crystal structure of human HNF1beta DNA binding domain in complex with a high-affinity promoter. Disease-causing mutations have been mapped to our structure, and their predicted effects have been tested by a set of biochemical/ functional studies. These findings together with earlier findings with a homologous protein HNF1alpha, help us to understand the structural basis of promoter recognition by these atypical POU transcription factors and the site-specific functional disruption by disease-causing mutations.
Figures



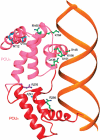



Similar articles
-
Two distinct teleost hepatocyte nuclear factor 1 genes, hnf1alpha/tcf1 and hnf1beta/tcf2, abundantly expressed in liver, pancreas, gut and kidney of zebrafish.Gene. 2004 Aug 18;338(1):35-46. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2004.05.003. Gene. 2004. PMID: 15302404
-
Regulation of the expression of human organic anion transporter 3 by hepatocyte nuclear factor 1alpha/beta and DNA methylation.Mol Pharmacol. 2006 Sep;70(3):887-96. doi: 10.1124/mol.106.025494. Epub 2006 Jun 22. Mol Pharmacol. 2006. PMID: 16793932
-
Structural and calorimetric studies demonstrate that the hepatocyte nuclear factor 1β (HNF1β) transcription factor is imported into the nucleus via a monopartite NLS sequence.J Struct Biol. 2016 Sep;195(3):273-281. doi: 10.1016/j.jsb.2016.06.018. Epub 2016 Jun 21. J Struct Biol. 2016. PMID: 27346421 Free PMC article.
-
Distinct roles of HNF1beta, HNF1alpha, and HNF4alpha in regulating pancreas development, beta-cell function and growth.Endocr Dev. 2007;12:33-45. doi: 10.1159/000109603. Endocr Dev. 2007. PMID: 17923767 Review.
-
Elucidating the Mutational Landscape in Hepatocyte Nuclear Factor 1β (HNF1B) by Computational Approach.Adv Protein Chem Struct Biol. 2017;107:283-306. doi: 10.1016/bs.apcsb.2016.11.005. Epub 2017 Jan 3. Adv Protein Chem Struct Biol. 2017. PMID: 28215227 Review.
Cited by
-
Human mutations affect the epigenetic/bookmarking function of HNF1B.Nucleic Acids Res. 2016 Sep 30;44(17):8097-111. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkw467. Epub 2016 May 26. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016. PMID: 27229139 Free PMC article.
-
Renal and Extrarenal Phenotypes in Patients With HNF1B Variants and Chromosome 17q12 Microdeletions.Kidney Int Rep. 2024 May 16;9(8):2514-2526. doi: 10.1016/j.ekir.2024.05.007. eCollection 2024 Aug. Kidney Int Rep. 2024. PMID: 39156164 Free PMC article.
-
Maturity-Onset Diabetes of the Young: Mutations, Physiological Consequences, and Treatment Options.J Pers Med. 2022 Oct 25;12(11):1762. doi: 10.3390/jpm12111762. J Pers Med. 2022. PMID: 36573710 Free PMC article. Review.
-
HNF1B Transcription Factor: Key Regulator in Renal Physiology and Pathogenesis.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Oct 2;25(19):10609. doi: 10.3390/ijms251910609. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39408938 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Residue correlation networks in nuclear receptors reflect functional specialization and the formation of the nematode-specific P-box.BMC Genomics. 2013;14 Suppl 6(Suppl 6):S1. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-14-S6-S1. Epub 2013 Oct 25. BMC Genomics. 2013. PMID: 24564869 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Yamagata K. Regulation of pancreatic beta-cell function by the HNF transcription network: lessons from maturity-onset diabetes of the young (MODY) Endocr. J. 2003;50:491–499. - PubMed
-
- Malecki MT. Genetics of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2005;68(Suppl 1):S10–21. - PubMed
-
- Giuffrida FM, Reis AF. Genetic and clinical characteristics of maturity-onset diabetes of the young. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2005;7:318–326. - PubMed
-
- Chakrabarti SK, Mirmira RG. Transcription factors direct the development and function of pancreatic beta cells. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2003;14:78–84. - PubMed
-
- Edghill EL, Bingham C, Slingerland AS, Minton JA, Noordam C, Ellard S, Hattersley AT. Hepatocyte nuclear factor-1 beta mutations cause neonatal diabetes and intrauterine growth retardation: support for a critical role of HNF-1beta in human pancreatic development. Diabetic Med. 2006;23:1301–1306. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

