Glucosamine affects intracellular signalling through inhibition of mitogen-activated protein kinase phosphorylation in human chondrocytes
- PMID: 17925024
- PMCID: PMC2212570
- DOI: 10.1186/ar2307
Glucosamine affects intracellular signalling through inhibition of mitogen-activated protein kinase phosphorylation in human chondrocytes
Abstract
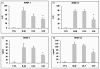
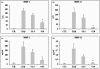
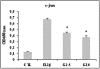
The aim of this study was to determine the effects of glucosamine on matrix metalloprotease (MMP) production, on mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) phosphorylation, and on activator protein (AP)-1 transcription factor activation in human chondrocytes. The human immortalized cell line lbpva55 and healthy human chondrocytes (obtained from healthy donors) were subjected to challenge with 10 ng/ml IL-1beta after pretreatment with 2.5 or 10 mmol/l glucosamine. MMP mRNA expression levels were evaluated using quantitative real-time PCR, and MMP protein production levels were evaluated in the culture supernatant using ELISA. MAPK phosphorylation was evaluated using Western blotting. AP-1 transcription factor activation was evaluated by measuring AP-1 DNA-binding activity. After IL-1beta stimulation, levels of MMP-1, MMP-3 and MMP-13 production were markedly increased. Treatment with 2.5 and 10 mmol/l glucosamine reduced expression of these metalloproteases. MMP expression is regulated by transcription factors such as the AP-1 complex, which is activated by phosphorylated MAPKs. IL-1beta stimulated phosphorylation of c-jun amino-terminal kinase, p38 MAPK and extracellular signal-regulated kinase-1/2. Glucosamine inhibited c-jun amino-terminal kinase and p38 phosphorylation, and consequently c-jun binding activity. These findings demonstrate, for the first time, that glucosamine inhibits IL-1beta-stimulated MMP production in human chondrocytes by affecting MAPK phosphorylation.
Figures


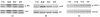
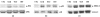
Similar articles
-
Chondroprotective effects of glucosamine involving the p38 MAPK and Akt signaling pathways.Rheumatol Int. 2008 Aug;28(10):1009-16. doi: 10.1007/s00296-008-0561-4. Epub 2008 Mar 14. Rheumatol Int. 2008. PMID: 18340449
-
MyD88, IRAK1 and TRAF6 knockdown in human chondrocytes inhibits interleukin-1-induced matrix metalloproteinase-13 gene expression and promoter activity by impairing MAP kinase activation.Cell Signal. 2007 Dec;19(12):2549-57. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2007.08.013. Epub 2007 Aug 25. Cell Signal. 2007. PMID: 17905570
-
Borrelia burgdorferi-induced expression of matrix metalloproteinases from human chondrocytes requires mitogen-activated protein kinase and Janus kinase/signal transducer and activator of transcription signaling pathways.Infect Immun. 2004 May;72(5):2864-71. doi: 10.1128/IAI.72.5.2864-2871.2004. Infect Immun. 2004. PMID: 15102798 Free PMC article.
-
Epigallocatechin-3-gallate selectively inhibits interleukin-1beta-induced activation of mitogen activated protein kinase subgroup c-Jun N-terminal kinase in human osteoarthritis chondrocytes.J Orthop Res. 2003 Jan;21(1):102-9. doi: 10.1016/S0736-0266(02)00089-X. J Orthop Res. 2003. PMID: 12507586
-
Phenyl N-tert-butylnitrone down-regulates interleukin-1 beta-stimulated matrix metalloproteinase-13 gene expression in human chondrocytes: suppression of c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase, p38-mitogen-activated protein kinase and activating protein-1.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2003 Jun;305(3):981-8. doi: 10.1124/jpet.102.048611. Epub 2003 Mar 6. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2003. PMID: 12626640
Cited by
-
The inflammatory circuitry of miR-149 as a pathological mechanism in osteoarthritis.Rheumatol Int. 2014 May;34(5):711-6. doi: 10.1007/s00296-013-2754-8. Epub 2013 Apr 18. Rheumatol Int. 2014. PMID: 23595570
-
Memory and synaptic plasticity are impaired by dysregulated hippocampal O-GlcNAcylation.Sci Rep. 2017 Apr 3;7:44921. doi: 10.1038/srep44921. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28368052 Free PMC article.
-
The N-Acetyl Phenylalanine Glucosamine Derivative Attenuates the Inflammatory/Catabolic Environment in a Chondrocyte-Synoviocyte Co-Culture System.Sci Rep. 2019 Sep 19;9(1):13603. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-49188-9. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31537813 Free PMC article.
-
L-carnitine enhances extracellular matrix synthesis in human primary chondrocytes.Rheumatol Int. 2013 Sep;33(9):2399-403. doi: 10.1007/s00296-012-2373-9. Epub 2012 Mar 27. Rheumatol Int. 2013. PMID: 22451022
-
The Hexosamine Biosynthetic Pathway as a Therapeutic Target after Cartilage Trauma: Modification of Chondrocyte Survival and Metabolism by Glucosamine Derivatives and PUGNAc in an Ex Vivo Model.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jul 6;22(14):7247. doi: 10.3390/ijms22147247. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34298867 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Reginster JY, Deroisy R, Rovati LC, Lee RL, Lejeune E, Bruyere O, Giacovelli G, Henrotin Y, Dacre JE, Gosset C. Long-term effects of glucosamine sulphate on osteoarthritis progression: a randomised, placebo-controlled clinical trial. Lancet. 2001;357:251–256. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(00)03610-2. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bruyere O, Honore A, Ethgen O, Rovati LC, Giacovelli G, Henrotin YE, Seidel L, Reginster JY. Correlation between radiographic severity of knee osteoarthritis and future disease progression. Results from a 3-year prospective, placebo-controlled study evaluating the effect of glucosamine sulfate. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2003;11:1–5. doi: 10.1053/joca.2002.0848. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

