miRNA profiling of naïve, effector and memory CD8 T cells
- PMID: 17925868
- PMCID: PMC2000354
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0001020
miRNA profiling of naïve, effector and memory CD8 T cells
Abstract
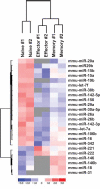
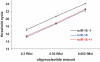
microRNAs have recently emerged as master regulators of gene expression during development and cell differentiation. Although profound changes in gene expression also occur during antigen-induced T cell differentiation, the role of miRNAs in the process is not known. We compared the miRNA expression profiles between antigen-specific naïve, effector and memory CD8+ T cells using 3 different methods--small RNA cloning, miRNA microarray analysis and real-time PCR. Although many miRNAs were expressed in all the T cell subsets, the frequency of 7 miRNAs (miR-16, miR-21, miR-142-3p, miR-142-5p, miR-150, miR-15b and let-7f) alone accounted for approximately 60% of all miRNAs, and their expression was several fold higher than the other expressed miRNAs. Global downregulation of miRNAs (including 6/7 dominantly expressed miRNAs) was observed in effector T cells compared to naïve cells and the miRNA expression levels tended to come back up in memory T cells. However, a few miRNAs, notably miR-21 were higher in effector and memory T cells compared to naïve T cells. These results suggest that concomitant with profound changes in gene expression, miRNA profile also changes dynamically during T cell differentiation. Sequence analysis of the cloned mature miRNAs revealed an extensive degree of end polymorphism. While 3'end polymorphisms dominated, heterogeneity at both ends, resembling drosha/dicer processing shift was also seen in miR-142, suggesting a possible novel mechanism to generate new miRNA and/or to diversify miRNA target selection. Overall, our results suggest that dynamic changes in the expression of miRNAs may be important for the regulation of gene expression during antigen-induced T cell differentiation. Our study also suggests possible novel mechanisms for miRNA biogenesis and function.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



Similar articles
-
Dynamically expressed microRNA-15b modulates the activities of CD8+ T lymphocytes in mice with Lewis lung carcinoma.J Transl Med. 2013 Mar 21;11:71. doi: 10.1186/1479-5876-11-71. J Transl Med. 2013. PMID: 23517578 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA regulation in human CD8+ T cell subsets--cytokine exposure alone drives miR-146a expression.J Transl Med. 2014 Oct 21;12:292. doi: 10.1186/s12967-014-0292-0. J Transl Med. 2014. PMID: 25331734 Free PMC article.
-
Differential expression of basal microRNAs' patterns in human dental pulp stem cells.J Cell Mol Med. 2015 Mar;19(3):566-80. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.12381. Epub 2014 Dec 5. J Cell Mol Med. 2015. PMID: 25475098 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of the MIR155 host gene in physiological and pathological processes.Gene. 2013 Dec 10;532(1):1-12. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2012.12.009. Epub 2012 Dec 14. Gene. 2013. PMID: 23246696 Review.
-
Adipogenic miRNA and meta-signature miRNAs involved in human adipocyte differentiation and obesity.Oncotarget. 2016 Jun 28;7(26):40830-40845. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.8518. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27049726 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
MicroRNA regulation and its effects on cellular transcriptome in human immunodeficiency virus-1 (HIV-1) infected individuals with distinct viral load and CD4 cell counts.BMC Infect Dis. 2013 May 30;13:250. doi: 10.1186/1471-2334-13-250. BMC Infect Dis. 2013. PMID: 23721325 Free PMC article.
-
Micro RNA Targets in HIV Latency: Insights into Novel Layers of Latency Control.AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 2021 Feb;37(2):109-121. doi: 10.1089/AID.2020.0150. Epub 2020 Nov 10. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 2021. PMID: 33045840 Free PMC article.
-
Systems Studies Uncover miR-146a as a Target in Leishmania major Infection Model.ACS Omega. 2020 May 18;5(21):12516-12526. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.0c01502. eCollection 2020 Jun 2. ACS Omega. 2020. PMID: 32548436 Free PMC article.
-
Glucocorticoids suppress T cell function by up-regulating microRNA-98.Arthritis Rheum. 2013 Jul;65(7):1882-90. doi: 10.1002/art.37966. Arthritis Rheum. 2013. PMID: 23575983 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNAs miR-17 and miR-20a inhibit T cell activation genes and are under-expressed in MS whole blood.PLoS One. 2010 Aug 11;5(8):e12132. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0012132. PLoS One. 2010. PMID: 20711463 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Murali-Krishna K, Altman JD, Suresh M, Sourdive DJ, Zajac AJ, et al. Counting antigen-specific CD8 T cells: a reevaluation of bystander activation during viral infection. Immunity. 1998;8:177–187. - PubMed
-
- Kaech SM, Wherry EJ, Ahmed R. Effector and memory T-cell differentiation: implications for vaccine development. Nat Rev Immunol. 2002;2:251–262. - PubMed
-
- Antia R, Ganusov VV, Ahmed R. The role of models in understanding CD8+ T-cell memory. Nat Rev Immunol. 2005;5:101–111. - PubMed
-
- Gourley TS, Wherry EJ, Masopust D, Ahmed R. Generation and maintenance of immunological memory. Semin Immunol. 2004;16:323–333. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

