Nonenzymatic detection of bacterial genomic DNA using the bio bar code assay
- PMID: 17927207
- PMCID: PMC3241528
- DOI: 10.1021/ac701626y
Nonenzymatic detection of bacterial genomic DNA using the bio bar code assay
Abstract
The detection of bacterial genomic DNA through a nonenzymatic nanomaterials-based amplification method, the bio bar code assay, is reported. The assay utilizes oligonucleotide-functionalized magnetic microparticles to capture the target of interest from the sample. A critical step in the new assay involves the use of blocking oligonucleotides during heat denaturation of the double-stranded DNA. These blockers bind to specific regions of the target DNA upon cooling and prevent the duplex DNA from rehybridizing, which allows the particle probes to bind. Following target isolation using the magnetic particles, oligonucleotide-functionalized gold nanoparticles act as target recognition agents. The oligonucleotides on the nanoparticle (bar codes) act as amplification surrogates. The bar codes are then detected using the Scanometric method. The limit of detection for this assay was determined to be 2.5 fM, and this is the first demonstration of a bar code-type assay for the detection of double-stranded, genomic DNA.
Figures
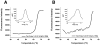
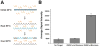
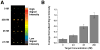
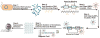
Similar articles
-
Nanoparticle based bio-bar code technology for trace analysis of aflatoxin B1 in Chinese herbs.J Food Drug Anal. 2018 Apr;26(2):815-822. doi: 10.1016/j.jfda.2017.11.003. Epub 2017 Dec 6. J Food Drug Anal. 2018. PMID: 29567253 Free PMC article.
-
PCR-free quantitative detection of genetically modified organism from raw materials. An electrochemiluminescence-based bio bar code method.Anal Chem. 2008 May 15;80(10):3566-71. doi: 10.1021/ac0713306. Epub 2008 Apr 3. Anal Chem. 2008. PMID: 18386909 Free PMC article.
-
A bio-bar-code assay based upon dithiothreitol-induced oligonucleotide release.Anal Chem. 2005 Dec 15;77(24):8174-8. doi: 10.1021/ac0514265. Anal Chem. 2005. PMID: 16351173
-
Bio-bar-code-based DNA detection with PCR-like sensitivity.J Am Chem Soc. 2004 May 19;126(19):5932-3. doi: 10.1021/ja049384+. J Am Chem Soc. 2004. PMID: 15137735
-
Genomic DNA labeling for hybridization with DNA arrays.Biotechniques. 2003 Apr;34(4):700-2, 704. doi: 10.2144/03344bm03. Biotechniques. 2003. PMID: 12703291 No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Single-Molecule FRET-Based Dynamic DNA Sensor.ACS Sens. 2021 Mar 26;6(3):1367-1374. doi: 10.1021/acssensors.1c00002. Epub 2021 Mar 15. ACS Sens. 2021. PMID: 33720708 Free PMC article.
-
Detection of blood-transmissible agents: can screening be miniaturized?Transfusion. 2010 Sep;50(9):2032-45. doi: 10.1111/j.1537-2995.2010.02678.x. Transfusion. 2010. PMID: 20546202 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Towards in vitro molecular diagnostics using nanostructures.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2012 Feb;69(3):373-88. doi: 10.1007/s00018-011-0855-7. Epub 2011 Oct 19. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2012. PMID: 22009454 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Highly rapid amplification-free and quantitative DNA imaging assay.Sci Rep. 2013;3:1852. doi: 10.1038/srep01852. Sci Rep. 2013. PMID: 23677392 Free PMC article.
-
Bio-barcode detection technology and its research applications: A review.J Adv Res. 2019 Apr 27;20:23-32. doi: 10.1016/j.jare.2019.04.009. eCollection 2019 Nov. J Adv Res. 2019. PMID: 31193255 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Saiki RK, Scharf S, Faloona F, Mullis KB, Horn GT, Erlich HA, Arnheim N. Science. 1985;230:1350–1354. - PubMed
-
- Mullis K, Faloona F, Scharf S, Saiki R, Horn G, Erlich H. Cold Spring Harbor Symposia on Quantitative Biology. 1986;51:263–273. - PubMed
-
- Scharf SJ, Horn GT, Erlich HA. Science. 1986;233:1076–1078. - PubMed
-
- Kary BM. Angew Chem Int Ed. 1994;33:1209–1213.
-
- Jochen-Wilhelm AP. ChemBioChem. 2003;4:1120–1128. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

