NKG2A inhibits TH2 cell effector function in vitro
- PMID: 17927829
- PMCID: PMC2174509
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2466-7-14
NKG2A inhibits TH2 cell effector function in vitro
Abstract
Background: We previously reported that NKG2A, a key inhibitory ligand for HLA-E, is expressed on activated TH2 but not TH1 cells. Here we measured cytokine expression in human ex vivo TH2 cells upon activation with anti-CD3/28 and challenge with an NKG2A-specific agonist.
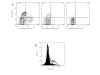
Methods: TH2 cells were purified from healthy volunteers and activated with anti-CD3/28 in the presence and absence of NKG2A-specific agonist. IL-4 was used as a marker of TH2 effector function and measured by flow cytometry.
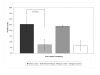
Results: Activation of TH2 cells increased NKG2A positivity from (Mean +/- SE) 7.3 +/- 2.4% to 13.7 +/- 3.8%; (p = 0.03). The presence of NKG2A agonist did not significantly alter NKG2A expression, however, the percentage of activated TH2 cells expressing intracellular IL-4 decreased from 25.5 +/- 6.8% to 9.3 +/- 4.8% (p = 0.001).
Conclusion: We show that signalling through NKG2A suppresses TH2 effector function. This may provide a means to modulate Th1/Th2 balance in diseases where Th2 cytokines predominate.
Figures
Similar articles
-
NKG2A and CD56 are coexpressed on activated TH2 but not TH1 lymphocytes.Hum Immunol. 2005 Dec;66(12):1223-34. doi: 10.1016/j.humimm.2006.02.005. Epub 2006 Mar 27. Hum Immunol. 2005. PMID: 16690409 Free PMC article.
-
Retinoic acids exert direct effects on T cells to suppress Th1 development and enhance Th2 development via retinoic acid receptors.Int Immunol. 2003 Aug;15(8):1017-25. doi: 10.1093/intimm/dxg101. Int Immunol. 2003. PMID: 12882839
-
GITR signaling potentiates airway hyperresponsiveness by enhancing Th2 cell activity in a mouse model of asthma.Respir Res. 2009 Oct 7;10(1):93. doi: 10.1186/1465-9921-10-93. Respir Res. 2009. PMID: 19811658 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms of bacillus Calmette-Guerin mediated natural killer cell activation.J Urol. 2004 Oct;172(4 Pt 1):1490-5. doi: 10.1097/01.ju.0000131944.52354.63. J Urol. 2004. PMID: 15371877
-
The cell biology of the human natural killer cell CD94/NKG2A inhibitory receptor.Mol Immunol. 2005 Feb;42(4):485-8. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2004.07.031. Mol Immunol. 2005. PMID: 15607803 Review.
References
-
- Lazetic S, Chang C, Houchins JP, Lanier LL, Phillips JH. Human natural killer cell receptors involved in MHC class I recognition are disulfide-linked heterodimers of CD94 and NKG2 subunits. J Immunol. 1996;157:4741–4745. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

