Beyond inflammation: airway epithelial cells are at the interface of innate and adaptive immunity
- PMID: 17928212
- PMCID: PMC2196222
- DOI: 10.1016/j.coi.2007.08.004
Beyond inflammation: airway epithelial cells are at the interface of innate and adaptive immunity
Abstract
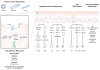
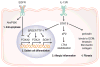
It has become increasingly clear that airway epithelial cells are central participants in innate and adaptive immune responses as well as mucosal inflammation. Epithelial cells produce antimicrobial host defense molecules, proinflammatory cytokines and chemokines in response to activation via pathogen recognition receptors. Recruitment of immune cells including dendritic cells, T cells and B cells into the proximity of epithelium results in the enhancement of adaptive immunity through interactions with epithelial cells. Newly identified epithelial-derived cytokines, including TSLP, IL-33 and BAFF, help to shape the local accumulation and activation of Th2 responses and B cell immunoglobulin production. Epithelial cells are also downstream targets of molecules that activate IL-13R and EGFR and are responsible for mucus production in both protective immune responses and allergic airway inflammatory diseases. Improved understanding of epithelial immune and inflammatory responses will hopefully suggest new strategies for therapeutic intervention.
Figures
References
-
- Akira S, Uematsu S, Takeuchi O. Pathogen recognition and innate immunity. Cell. 2006;124:783–801. This review describes the mechanism of pathogen recognition by PRRs including TLRs. - PubMed
-
- Lee MS, Kim YJ. Signaling pathways downstream of pattern-recognition receptors and their cross talk. Annu Rev Biochem. 2007;76:447–80. - PubMed
-
- Trinchieri G, Sher A. Cooperation of Toll-like receptor signals in innate immune defence. Nat Rev Immunol. 2007;7:179–190. - PubMed
-
- Sha Q, Truong-Tran AQ, Plitt JR, Beck LA, Schleimer RP. Activation of airway epithelial cells by toll-like receptor agonists. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2004;31:358–364. - PubMed
-
- Homma T, Kato A, Hashimoto N, Batchelor J, Yoshikawa M, Imai S, Wakiguchi H, Saito H, Matsumoto K. Corticosteroid and cytokines synergistically enhance toll-like receptor 2 expression in respiratory epithelial cells. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2004;31:463–469. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

