X box binding protein XBP-1s transactivates the Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus (KSHV) ORF50 promoter, linking plasma cell differentiation to KSHV reactivation from latency
- PMID: 17928342
- PMCID: PMC2168861
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.01663-07
X box binding protein XBP-1s transactivates the Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus (KSHV) ORF50 promoter, linking plasma cell differentiation to KSHV reactivation from latency
Abstract
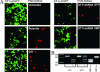
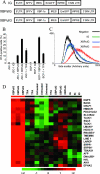
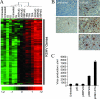
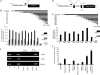
Reactivation of lytic replication from viral latency is a defining property of all herpesviruses. Despite this, the authentic physiological cues for the latent-lytic switch are unclear. Such cues should ensure that viral lytic replication occurs under physiological conditions, predominantly in sites which facilitate transmission to permissive uninfected cells and new susceptible hosts. Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus (KSHV) is associated with the B-cell neoplasm primary effusion lymphoma (PEL), in which the virus remains latent. We have previously shown that PEL cells have the gene expression profile and immunophenotype of cycling preplasma cells (plasmablasts). Here, we show that the highly active spliced isoform of plasma cell transcription factor X box binding protein 1 (XBP-1s) is a lytic switch for KSHV. XBP-1s is normally absent in PEL, but the induction of endoplasmic reticulum stress leads to XBP-1s generation, plasma cell-like differentiation, and lytic reactivation of KSHV. XBP-1s binds to and activates the KSHV immediate-early gene ORF50 and synergizes with the ORF50 gene product RTA to induce a full lytic cycle. These data suggest that KSHV remains latent until B-cell terminal differentiation into plasma cells, the transcriptional environment of which provides the physiological "lytic switch" through XBP-1s. This links B-cell terminal differentiation to KSHV lytic reactivation.
Figures

References
-
- An, J., Y. Sun, M. Fisher, and M. B. Rettig. 2004. Antitumor effects of bortezomib (PS-341) on primary effusion lymphomas. Leukemia 18:1699-1704. - PubMed
-
- Bertolotti, A., Y. Zhang, L. M. Hendershot, H. P. Harding, and D. Ron. 2000. Dynamic interaction of BiP and ER stress transducers in the unfolded-protein response. Nat. Cell Biol. 2:326-332. - PubMed
-
- Calfon, M., H. Zeng, F. Urano, J. H. Till, S. R. Hubbard, H. P. Harding, S. G. Clark, and D. Ron. 2002. IRE1 couples endoplasmic reticulum load to secretory capacity by processing the XBP-1 mRNA. Nature 415:92-96. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

